Before diving into the details, it's vital to understand that international private jet charter involves numerous complex elements beyond simply booking an aircraft. This comprehensive guide covers critical aspects of international private aviation, from planning and regulatory compliance to customs procedures and hidden costs. Whether you're a seasoned private flyer or planning your first international charter, understanding these intricacies will help ensure a smooth, compliant journey while avoiding common pitfalls that can disrupt travel plans or lead to unexpected expenses.
Understanding the International Private Jet Charter Landscape
The private jet charter industry operates under strict regulatory frameworks that vary significantly from country to country. When flying internationally from the United States, you'll encounter a complex web of regulations, permits, and procedures designed to ensure safety, security, and proper oversight of aviation activities across borders. These frameworks continually evolve, requiring operators and passengers to stay informed of current requirements for compliant travel.
International private jet travel offers substantial benefits over commercial flights, including flexibility, privacy, and access to smaller airports closer to your final destination. However, these advantages come with additional responsibility to navigate international aviation regulations, customs requirements, and associated costs that often surprise first-time international charter clients.
The foundation of a successful international charter begins with understanding the relationship between operators (companies that actually fly the aircraft), brokers (intermediaries who arrange flights), and regulatory bodies like the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the US or equivalent authorities abroad. This relationship establishes the framework for every aspect of your journey, from flight permits to customs clearance.
Broker vs. Operator Relationships: A Critical Distinction
One of the most significant traps in private jet charter is confusion about the roles and responsibilities of charter brokers versus Part 135 operators. This ambiguity can lead to serious accountability issues and potential safety risks. Some brokers blur the lines between being intermediaries and actual aircraft operators, using terminology like "our fleet" or "our pilots" in marketing materials. This creates a false perception that you're contracting directly with an aircraft operator when you're actually dealing with a middleman.
When problems arise during international travel, this confusion can make it difficult to determine who is ultimately responsible. Part 135 operators are subject to rigorous FAA oversight and safety standards, while brokers may not adhere to these strict regulations. Understanding this distinction becomes even more critical for international flights, as regulatory compliance across borders adds another layer of complexity.
Selecting Your Destination and Travel Companions
The first step in planning an international private jet charter is determining your destination and who will be traveling with you. Your group size directly impacts the aircraft you'll need, affecting both cost and operational considerations for international travel. Smaller groups may enjoy more destination options, including access to smaller airports with limited facilities for larger aircraft.
Your destination choice significantly impacts the complexity of your journey. Flying to popular destinations like the Caribbean or Mexico involves different regulatory requirements and costs compared to more remote or restricted destinations in Asia or the Middle East. Each country has unique entry requirements, overflight permissions, and landing permits that must be secured before departure.
Setting a Realistic Budget for an International Charter
International private jet charter costs extend well beyond the basic hourly rate of aircraft operation. When establishing your budget, consider all potential expenses, including international fees that vary by destination. For example, flights from the US to the Caribbean typically incur about $1,700 in international fees. At the same time, Mexico costs approximately $2,500, and flights to parts of Asia can reach $10,000 in additional international fees alone.
These international fees comprise handling costs, customs charges, and other expenses paid directly to foreign authorities. Unlike domestic flights that incur a 7.5% Federal Excise Tax, international flights face these country-specific charges that cannot be avoided or negotiated. Understanding these costs upfront prevents budgetary surprises and helps set realistic expectations for your international journey.
Selecting a Reputable Charter Provider
Working with a knowledgeable, reputable charter broker or operator is perhaps the most important decision for international travel. The right partner will navigate complex regulations, secure necessary permits, and ensure compliance with both US and foreign requirements. When evaluating potential charter companies, look for those with extensive international experience and established relationships with operators worldwide.
Verify that your chosen provider works only with operators certified under Part 135 regulations by the FAA (for US operators) or equivalent foreign civil aviation authorities. These certifications ensure adherence to strict safety standards, proper maintenance protocols, and crew training requirements essential for international operations.
Avoiding Overpaying for International Charters
A common pitfall in international charter is overpaying due to inadequate comparison shopping or selecting inappropriate aircraft. Less experienced charter customers often choose aircraft that are too large or too small for their mission, unnecessarily increasing costs.
To avoid overpaying, obtain multiple quotes from different brokers or operators and ensure the quotes include all potential international fees for your specific destination. The charter market can be non-transparent and confusing, so thorough research and comparison shopping are essential.
Remember that charter price calculations are highly individualized, depending on the operator's sales department, management contracts with aircraft owners, fleet utilization, and more. A good broker advocates for clients while still making a profit margin on bookings.
Regulatory Requirements and Documentation for International Flights
Essential Aviation Permits
International private jet flights require various permits that must be secured before departure. These permissions govern your ability to enter, exit, or traverse foreign airspace and are managed by each country's national civil aviation authority.
Three primary permit types are necessary for international operations:
- Overflight Permits: The authorization to fly over a country's airspace without landing protects national sovereignty and ensures air traffic safety.
- Landing Permits: Permission to land at designated airports within a foreign country, ensuring the facility can accommodate your aircraft type and purpose.
- Special Operations Permits: These are additional authorizations for non-standard flights, such as medical evacuations, humanitarian missions, or oversized cargo transport.
The process for obtaining these permits varies by country and is constantly changing. For example, Mexico recently modified its permit requirements in 2024, affecting private and charter operations. These changes impact everything from application procedures to documentation requirements.
Documentation Requirements for International Travel
All international flights require extensive documentation for both the aircraft and passengers. The aircraft must carry effective certificates of registration and a valid airworthiness certificate, while passengers need valid passports and potentially visas depending on the destination country's requirements.
According to FAA regulations, aircraft conducting international operations must carry several mandatory documents. These include the general declaration, passenger manifest, and cargo manifest. Additionally, operators must prepare and maintain proper customs forms, immigration forms, and agricultural and quarantine declarations for international border crossings. These comprehensive documentation requirements ensure compliance with both departure and arrival country regulations.
These documents must follow the ICAO standard format and be provided in English to ensure consistent interpretation by authorities worldwide. Regulatory agencies typically require supplementary information beyond standard documentation for non-scheduled flights, which encompass most private charter operations. This additional information commonly includes detailed aircraft specifications, explicit purpose of the flight, complete routing information with intermediate stops, and specific charter arrangement details. Experienced operators maintain document templates and checklists to ensure all paperwork meets the exact specifications of each country involved in the journey.
Compliance with International Regulations
Private jet operators must comply with the regulations of every country involved in the journey, departure, and arrival, as well as any countries through which they pass. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) establishes global standards, but individual countries implement specific requirements.
In the United States, the FAA governs private aviation through Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs), particularly Parts 135 (commercial operators) and Part 91 (private operators). These regulations address aircraft maintenance, crew qualifications, and flight operations. When traveling internationally, operators must also adhere to the equivalent regulations in destination countries.
Understanding these regulatory frameworks ensures your flight meets all legal requirements and avoids potential delays, fines, or even flight cancellations due to non-compliance.
Customs and Immigration Procedures for International Private Flying
Entry Requirements and Processes
When arriving in a foreign country by private jet, all passengers and crew must clear customs and immigration, just as they would on commercial flights. The difference lies in the facilities and efficiency of the process. Many international airports offer dedicated customs facilities for private jet passengers, streamlining the entry process.
Every country has unique entry requirements that must be met before arrival. These requirements impact what you can bring with you and how the clearance process works. Most countries require advance passenger information before arrival, allowing authorities to pre-screen travelers. This information typically includes passport details, flight information, and purpose of visit.
Upon landing at an international destination, passengers must present valid passports and, if required, visas to immigration officers. Following immigration, customs officials may inspect luggage and any declared items. The process varies by country, with some requiring face-to-face interviews while others implement more streamlined electronic systems.
Pre-Arrival Notification Requirements
Most countries require advance notification of private flights entering their airspace. This notification, often called an Advance Passenger Information System (APIS) submission, typically includes:
- Passenger and crew information
- Aircraft details
- Flight routing
- Estimated arrival time
- Purpose of visit
This information must be submitted within specified timeframes before arrival, which vary by country. Failure to provide accurate or timely information can result in denied entry, fines, or significant delays upon arrival.
Special Considerations for Bringing Items Internationally
Customs regulations govern what items can be brought into a country. Restrictions typically apply to:
- Currency (amounts exceeding specified limits must be declared)
- Food and agricultural products
- Alcohol and tobacco
- Medications and pharmaceuticals
- Wildlife products and cultural artifacts
Understanding these restrictions before departure helps avoid confiscation of items, fines, or even criminal penalties in extreme cases. Unlike commercial flights where responsibility often falls on individual passengers, private jet operators and clients share responsibility for customs compliance.
Understanding Fees and Costs for International Private Jet Charter
Federal Excise Taxes vs. International Fees
When flying domestically within the United States, private jet charters are subject to a 7.5% Federal Excise Tax (FET) designed to cover air traffic control and other FAA services. However, international flights from the US face a different fee structure consisting of specific international fees that vary by destination.
These international fees combine handling costs, customs charges, and other expenses paid to foreign authorities. Unlike FET, which is percentage-based, international fees are fixed amounts determined by the destination country, though they may vary based on aircraft size and weight.
Destination-Specific International Fees
International fees vary significantly depending on your destination. These international fees represent only the mandatory government and regulatory charges for crossing borders - not the total cost of chartering an aircraft. They are additional expenses beyond the basic aircraft rental costs.
For travelers departing from the United States in 2025, an International Head Tax of $22.20 per passenger applies to any international flight leg that begins or ends in the US. Beyond this baseline tax, each region has specific supplemental fees:
Caribbean islands: approximately $1,700 in international fees, Mexico: approximately $2,500 in international fees and parts of Asia: up to $10,000 in international fees
Beyond basic international fees, several other costs impact international private jet charters. Landing fees constitute a significant expense that varies widely by airport and aircraft size, with premier destinations like London Heathrow or Tokyo Narita commanding premium rates compared to smaller regional airports. Navigation fees apply when using a country's air traffic control system, calculated based on distance traveled and aircraft weight. Ground services at international airports incur handling fees, which cover everything from aircraft marshalling to passenger transportation within the terminal area.
Customs fees for processing entry and exit documentation represent another unavoidable expense, while security fees apply in certain countries, like Canada's $1,000 security fee that applies universally to private aviation. Some regions implement additional specialized charges: the UK's Air Passenger Duty, France's Civil Aviation Tax, and Italy's Luxury Tax for private aviation.
Aircraft size significantly affects many of these fees, with larger jets typically incurring higher costs based on weight - a Gulfstream G650 will generally pay more in landing and navigation fees than a Citation CJ3. However, per-passenger costs like customs charges remain consistent regardless of aircraft size, creating economic efficiency for larger travel parties who can distribute these fixed expenses across more passengers.
For European destinations, destination-specific fees include various country-specific charges such as landing permits, overflight permits, and passenger taxes. For example, Italy imposes a luxury tax of 100 euros per passenger for flights up to 932 miles (1500 km) and 200 euros per passenger for longer flights. The UK charges an Air Passenger Duty that will increase to a maximum of £1,000 ($1,260) per passenger starting April 2026.
Middle Eastern destinations have their own fee structures, including sector fees in the UAE ranging from $60 to $105, depending on aircraft weight, and overflight charges from $130 to $235. Saudi Arabia and Bahrain calculate air navigation charges based on aircraft weight and distance, with surcharges for overflights.
These destination-specific fees are relatively stable throughout the year and are mandatory charges passed directly from the destination country to the operator, broker, or client. They typically include landing permits, overflight permits, customs charges, and immigration fees required by your route and arrival country.
Sample Cost Breakdown: New York to London (10 passengers on a Large Jet)
| Cost Component | Approximate Amount | Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Base Aircraft Charter | $95,000 | 75% |
| Fuel Surcharge | $12,000 | 10% |
| Crew Expenses | $3,500 | 3% |
| International Fees | $8,500 | 7% |
| Catering | $3,000 | 2% |
| Ground Transportation | $2,000 | 2% |
| Miscellaneous | $1,000 | 1% |
| TOTAL CHARTER COST | $125,000 | 100% |
The sample cost breakdown for a New York to London flight on a large jet provides a valuable baseline understanding of international charter economics, but these percentages fluctuate significantly based on route characteristics and aircraft selection. Understanding these variations helps clients anticipate how their specific charter scenario might differ from the standard model.
Here's an expanded analysis of how cost percentages shift across different routes and aircraft types, with specific examples to enhance practical application:
Key Variables Impacting Percentage Distribution
- Route Distance:
- Short-Haul (NYC-Nassau):
- Base Charter: 65-70% (lower flight time)
- Fuel: 5-8%
- International Fees: 15-20% (fixed $1,700 becomes larger proportion)
- Example: $50,000 total = $1,700 represents 3.4% → 15% in $11k total
- Ultra-Long Haul (LAX-Singapore):
- Base Charter: 60-65%
- Fuel: 20-25%
- Crew: 8-10% (required rest periods)
- International Fees: 3-5% ($10k in $300k total)
- Short-Haul (NYC-Nassau):
- Aircraft Class:
- Light Jet (Cessna Citation CJ4):
- Base Charter: 80-85%
- Fuel: 7-9%
- International Fees: 4-6%
- VIP Airliner (Boeing BBJ):
- Base Charter: 50-55%
- Crew: 12-15% (additional flight attendants)
- Catering: 8-10%
- International Fees: 2-3%
- Light Jet (Cessna Citation CJ4):
- Cargo vs. Passenger:
- Cargo Operations:
- Fuel: +5-7% (heavier payloads)
- Handling Fees: +3-5% (special equipment)
- International Fees: Same absolute $, but higher % if lower total
- Cargo Operations:
- Seasonal Variations:
- Peak Season (December Caribbean):
- Base Charter: +10-15%
- International Fees: Percentage decreases as base cost rises
- Winter Operations:
- De-icing: New 5-7% category
- Fuel: +3-5%
- Peak Season (December Caribbean):
Comparative Scenario Table
| Scenario | NYC-London (Heavy) | NYC-Nassau (Midsize) | LAX-Tokyo (Ultra LR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cost | $125,000 | $68,000 | $310,000 |
| Base Aircraft | 75% | 70% | 62% |
| Fuel | 10% | 12% | 22% |
| Crew | 3% | 4% | 8% |
| International Fees | 7% | 15% | 3% |
| Catering/Ground | 4% | 6% | 4% |
| Position/Empty Leg | N/A | 8% | 1% |
Critical Percentage Shift Patterns
- Inverse Relationship: As base costs increase with aircraft size/distance, international fees' percentage decreases despite fixed absolute costs
- Threshold Effects: Flights under 2 hours see international fees dominate (15-25%), while 8+ hour flights dilute them to 2-5%
- Regional Variations: European flights average 9-12% in combined fees vs. Middle East 6-8% due to different fee structures
- Cargo Impact: Reduces catering costs (0-1%) but increases fuel/handling percentages by 3-5%
This framework enables charter clients to:
- Anticipate how aircraft selection impacts cost structure
- Budget more accurately for different destination types
- Negotiate contracts understanding where fees are fixed vs. variable
- Optimize group size relative to fee allocation per passenger
Would you like specific calculations for a particular route/aircraft combination?
Aircraft Type Impact on Cost Structure
When shifting from large jets to smaller aircraft categories, the percentage allocation changes notably:
For light jets, the base charter percentage typically increases to 80-85% of total costs, as these aircraft have lower absolute costs for crew and catering. However, for ultra-long-range aircraft like the Gulfstream G700 (approximately $18,000/hour), fuel surcharges can rise to 15-20% of total costs due to their higher consumption rates.
International fees remain relatively fixed regardless of aircraft size, meaning they represent a higher percentage of total costs for light jets (potentially 10-12%) versus large jets (7% in our example) or ultra-long-range jets (as low as 5-6%).
Regional Variations in Cost Components
The search results reveal significant regional pricing differences. For example, the same Challenger 601 operating in South America costs approximately $13,000 more than in the United States for similar flight times, demonstrating how regional factors shift the breakdown.
For Caribbean destinations, international fees ($1,700) represent a smaller percentage of total costs compared to Asian routes where these fees can reach $10,000, potentially doubling their percentage share of the total from 7% to 14% or higher.
Middle Eastern routes see a shift toward higher security and handling fees. The UAE's weight-based sector fees ($60-$105) and overflight charges ($130-$235) mean larger aircraft allocate a greater percentage to these components.
Route-Specific Percentage Shifts
Transcontinental routes dramatically alter the breakdown. For Los Angeles to London ($140,000-$160,000), fuel becomes a much larger component, potentially reaching 15-18% of total costs due to the extended flight time and required reserves.
Short international routes (like Toronto to New York at $18,000-$21,600 for a light jet) see ground transportation and handling fees taking a proportionally larger slice of the pie-potentially 5-7% versus our example's 2%.
The sample breakdown reflects optimal conditions. In practice, seasonal factors can cause significant shifts, with winter operations in northern destinations potentially adding 3-5% to the total cost in de-icing charges alone.
Understanding these variable cost structures allows charter clients to better anticipate total expenses based on their specific travel parameters rather than relying on standardized percentages that may not reflect their particular routing, aircraft choice, or seasonal considerations.
Dynamic Pricing Structures and Hidden Fees
The pricing structure for international private jet charters often involves dynamic and non-transparent elements, with quotes that appear comprehensive at first glance but frequently exclude critical costs. Common hidden fees include de-icing charges, which become particularly relevant during winter operations at northern airports, and crew overnight expenses incurred when flight schedules require teams to stay at international locations. Catering costs for premium in-flight meals and beverages often appear as line-item surprises, while international handling fees for ground services at foreign airports can vary unpredictably based on local regulations. Customs overtime charges apply to flights arriving outside standard business hours, requiring additional payments to clear officials during evenings, weekends, or holidays.
To mitigate financial surprises, clients should insist on fully inclusive quotes that explicitly account for all potential international fees specific to their planned route and aircraft type. These quotes must be provided in writing with granular breakdowns of operational costs, seasonal surcharges, and country-specific levies. Special attention should be given to itineraries involving multiple jurisdictions or off-hours operations, as these scenarios frequently trigger cascading fees that inflate baseline estimates. Seasonality further complicates pricing, with winter de-icing requirements and summer peak surcharges at popular destinations necessitating advance disclosure in cost projections.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Broker vs. Operator Ambiguity
As mentioned earlier, confusion between brokers and operators represents a significant pitfall in private jet charter. When chartering internationally, this confusion can lead to serious issues with regulatory compliance and safety oversight. To avoid this pitfall, always clarify whether you're working with a broker or direct operator, and ensure your broker discloses the actual Part 135 operator conducting your flight.
Verify the operating certificate and insurance coverage of the actual aircraft operator before booking, especially for international flights where regulatory requirements are more complex. If a broker uses possessive terminology like "our aircraft" or "our pilots," request clarification about their exact relationship with the operator.
Backup Aircraft Logistics for International Missions
Mechanical issues can affect any aircraft, but addressing them internationally presents unique challenges. International recovery options are limited by the same permit and regulatory requirements that govern your original flight. When mechanical issues arise abroad, securing a replacement aircraft requires new permits, potentially causing significant delays.
To mitigate this risk, work with operators or brokers who maintain international recovery plans, including relationships with foreign operators who can provide backup aircraft if needed. Discuss contingency plans before departure, including potential costs for replacement aircraft in various international locations.
Documentation Requirements and Errors
Incomplete or incorrect documentation represents one of the most common causes of delays and disruptions in international private jet travel. Even minor errors on passenger information, permit applications, or aircraft documentation can result in denied entry, fines, or operational restrictions23.
To avoid documentation pitfalls, travelers must adopt a rigorous verification process that begins with confirming passport validity extends at least six months beyond the planned return date-a requirement many countries enforce strictly to prevent entry denials. Visa prerequisites should be confirmed through direct consultation with destination-country embassies or experienced aviation providers, as regulations frequently change and often include nuanced exemptions for private flight passengers.
Providing precise passenger details for permit applications is critical, as even minor discrepancies in names, birthdates, or passport numbers can trigger delays or fines. Operators must maintain current aircraft documentation including valid certificates of registration, airworthiness, and insurance, while clients should independently verify these materials' compliance with destination-country requirements.
Before submission, conduct thorough reviews of all paperwork through dual-channel verification-ideally involving both the charter provider and an independent aviation compliance specialist-to catch errors in complex forms like general declarations, cargo manifests, and agricultural clearance documents. This multilayered approach becomes particularly vital when operating in regions with stringent aviation controls, where authorities may impose severe penalties for incomplete or inaccurate filings.
Ground Coordination Failures
International private jet travel extends beyond the flight itself to include ground transportation, accommodations, and other services at your destination. Coordination failures between these elements can disrupt otherwise smooth journeys. Time zone differences, language barriers, and unfamiliar customs regulations contribute to coordination challenges that often catch first-time international charter clients unprepared. When ground logistics break down, even perfectly executed flights can result in frustrating experiences, from being stranded without appropriate transportation to facing unexpected delays clearing customs.
To prevent ground coordination issues, work with providers experienced in your specific destination who can arrange comprehensive ground services. These providers coordinate customs and immigration logistics to streamline entry processes, arrange appropriate ground transportation matching your group size and luggage requirements, and secure necessary security services for high-risk destinations or high-profile travelers. They also manage catering requirements for both in-flight and ground experiences, ensuring dietary restrictions and preferences are accommodated throughout your journey. Additionally, experienced providers align hotel arrangements with flight schedules, accounting for potential delays and ensuring accommodations remain available regardless of arrival time fluctuations.
Confirm all ground arrangements before departure and ensure you have local contact information for key service providers at your destination. Having direct lines of communication with ground handlers, customs facilitators, and transportation providers creates redundancy in your coordination plan, allowing for real-time adjustments when unexpected circumstances arise. This proactive approach to ground coordination significantly reduces the likelihood of disruptions and enhances the seamless experience that private aviation clients expect.
Selecting the Right Aircraft and Operator for International Missions
Aircraft Selection Considerations
Choosing the appropriate aircraft for international missions requires balancing range capabilities, passenger capacity, comfort requirements, and operational limitations. Longer international routes require aircraft with sufficient range to complete the journey with appropriate fuel reserves, while passenger capacity must accommodate your group size and luggage requirements.
International operations introduce additional considerations beyond standard aircraft selection, creating a complex evaluation matrix when selecting appropriate aircraft for global missions. Aircraft age and equipment specifications become paramount concerns as certain countries restrict entry of older aircraft based on stringent environmental and safety standards, particularly in Europe and parts of Asia where aging fleets face heightened scrutiny.
Noise certification emerges as a critical factor when operating to European destinations, where Stage 3 or preferably Stage 4 compliance is mandatory at most major airports. Aircraft lacking proper noise certifications may face operational restrictions, including limited landing times or outright bans at noise-sensitive airports like London City, Zurich, or Nice.
Avionics capabilities determine an aircraft's suitability for transoceanic navigation, requiring advanced systems like FANS (Future Air Navigation System), CPDLC (Controller-Pilot Data Link Communications), and enhanced weather radar for crossing vast oceanic regions safely. For lengthy international flights, cabin amenities become essential considerations for passenger comfort and well-being, with proper sleeping accommodations, multiple lavatories, and comprehensive galley facilities enabling meal preparation during flights that may exceed 10 hours in duration.
Evaluating Operator Qualifications
Not all private jet operators possess the experience and certifications necessary for international operations. When selecting an operator for international flights, thorough vetting becomes essential to ensure both safety and operational efficiency across borders. The foundation of this evaluation begins with verifying FAA certification under Part 135 for US operators, which establishes compliance with stringent safety standards beyond those required for private or corporate flight departments.
International operating experience in your specific destination region provides crucial insights that cannot be replicated through regulatory compliance alone. Operators with established flight histories to your intended destinations understand local protocols, cultural considerations, and operational nuances that can significantly impact flight execution and passenger experience.
Safety ratings and accreditations from independent third-party organizations like ARGUS Platinum or IS-BAO Stage 3 certification provide objective verification of an operator's safety management systems and operational excellence. These credentials require rigorous audits and ongoing compliance monitoring, distinguishing truly professional operators from those meeting only minimum standards.
Insurance coverage specifically designed for international operations protects against unique liabilities and risks encountered outside domestic airspace, while demonstrated experience with specific permit requirements for your destination prevents delays and complications during critical planning phases. Operators with established international experience navigate these complexities more effectively, as their familiarity with international procedures, documentation requirements, and potential challenges contributes significantly to smooth operations.
Using Charter Directories and Resources
Several resources can help identify qualified operators and appropriate aircraft for international missions. The Air Charter Guide stands as a foundational resource, providing comprehensive contact and fleet details for commercially licensed aircraft operators across 148 countries worldwide. This extensive database enables clients to identify potential operators with specific aircraft types and operational capabilities suited to their international travel requirements.
ARGUS safety ratings offer standardized evaluations of charter operators through a tiered system (Gold, Gold+, Platinum, Platinum+) that reflects operational safety, management systems, and regulatory compliance. These ratings provide objective measurements of operator quality beyond marketing claims or superficial credentials.
Wyvern safety reports deliver detailed analyses of specific charter operators through their PASS (Pilot and Aircraft Safety Survey) program, which examines pilot qualifications, aircraft maintenance records, and operational protocols against established industry best practices. These reports enable clients to make data-driven decisions when selecting international charter providers.
Aviation International News (AIN) publishes operator surveys that capture customer satisfaction metrics and operational performance indicators across the charter industry. These peer-based evaluations highlight operators consistently delivering exceptional international service while identifying potential concerns for discerning clients.
Regional aviation authorities' operator databases provide official verification of licensing status and regulatory compliance specific to different global regions. These resources help verify operator credentials, safety records, and international operating capabilities, providing additional assurance beyond basic web searches or referrals when selecting partners for complex international missions.
Planning for Successful International Private Jet Travel
Advance Planning Timelines for International Private Jet Charters
Below is a structured guide to advance planning requirements for different destinations, synthesized from regulatory guidelines, operator recommendations, and seasonal considerations. These timelines account for permit acquisition, aircraft availability, and operational logistics.
Standard Planning Windows by Region
| Destination Type | Minimum Lead Time | Ideal Lead Time | Critical Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caribbean/Mexico/Canada | 7 days | 14–21 days | Overflight permits, basic customs declarations |
| Europe | 14 days | 21–30 days | Noise certifications, EU VAT compliance |
| Middle East | 21 days | 30–45 days | Security clearances, cultural permits |
| Asia-Pacific | 21 days | 45–60 days | Agricultural restrictions, diplomatic permits |
| Remote/Restricted | 30 days | 60–90 days | Military zone approvals, special cargo permits |
Key Factors Influencing Timelines
-
Permit Processing
- Europe: Landing permits for EU destinations require 5–7 business days, but Italy/France demand 10–14 days for luxury tax compliance.
- Middle East: UAE/Saudi Arabia mandate 10-day lead times for外交 overflight permits due to heightened security protocols.
- Asia: China and India require 15–20 days for diplomatic slot approvals at major hubs like Beijing and Mumbai.
-
Seasonal Demand
- Peak Seasons:
- Caribbean (Dec–Mar): +7 days to standard timelines
- European Summer (Jun–Aug): +14 days for popular destinations like Nice/Mykonos
- Middle East (Nov–Feb): +10 days during Dubai Airshow/Saudi F1 Grand Prix
- Peak Seasons:
-
Event-Driven Surges
Event Destination Recommended Booking Cannes Film Festival Nice, France 6–9 months Monaco Grand Prix Monte Carlo 8–12 months Dubai Expo UAE 4–6 months Tokyo Olympics Japan 12+ months -
Aircraft-Specific Requirements
- Large Jets (G650/Falcon 8X): Add 7–10 days for weight-based slot allocations at congested airports.
- Older Aircraft: +14 days for noise certification renewals in EU/UK.
- Heavy Cargo: +21 days for oversized load permits in Asia/Middle East.
Last-Minute Flexibility
While 75% of private flights are booked within 2 weeks of departure (Source 7), last-minute international trips face constraints:
- 72-Hr Window: Possible for Caribbean/Canada with pre-vetted operators, but +25–40% cost surge.
- 48-Hr Window: Middle East/Asia require $15k–$25k expedited permit fees.
- 24-Hr Window: Only viable for emergency MEDEVAC flights with government coordination.
Critical Path Checklist
- 60+ Days Out: Secure diplomatic permits for restricted zones (e.g., Russia, North Korea).
- 30 Days Out: Finalize aircraft noise certifications for EU Stage 4 compliance.
- 14 Days Out: Submit finalized passenger manifests for APIS/Advance Passenger Information.
- 72 Hrs Out: Confirm fuel availability at remote destinations (e.g., Maldives, Seychelles).
Pro Tip: For complex itineraries (e.g., New York → Paris → Dubai), work backward from the most restrictive destination’s requirements. Middle Eastern permits often dictate timelines for multi-region trips. Always partner with brokers holding ARC/IATA certifications to navigate overlapping regulations.
Weather and Seasonal Considerations
International operations introduce weather and seasonal factors that vary dramatically from domestic flying. Hurricane seasons in the Caribbean, monsoons in Asia, and winter conditions in Europe all impact private jet operations differently than domestic weather patterns. These conditions affect not only flight safety but also permit processing, ground operations, and potential delays.
Seasonal events and holidays in destination countries can also impact private jet operations through airport congestion, handling delays, and accommodation availability. Planning international travel during major festivals or holidays may require additional lead time and expense.
Communication Plans and International Connectivity
Maintaining communication during international travel presents challenges not encountered domestically. Time zone differences spanning multiple continents can create scheduling complexities when trying to reach operators or service providers during their business hours. Language barriers introduce additional complications, particularly in regions where English proficiency varies significantly among ground service personnel. Varying telecommunication standards, network compatibility issues, and connectivity gaps in remote destinations further compound these challenges, creating potential communication breakdowns at critical moments during international journeys.
Establishing clear communication protocols before departure provides essential structure for managing these variables effectively. These protocols should define primary and secondary communication channels, escalation procedures for urgent matters, and predetermined check-in schedules that account for international time differences. Creating a communications matrix that maps key contacts to specific scenarios ensures efficient problem-solving during time-sensitive situations like weather diversions, mechanical issues, or customs delays.
Local contact information for ground handlers at each destination becomes invaluable when addressing airport-specific challenges or coordinating last-minute changes to arrival procedures. Time zone-appropriate communication windows should be established with all service providers, identifying optimal times for routine updates that respect business hours across different regions.
Backup communication methods including satellite phones, international mobile plans, and web-based messaging platforms create redundancy when primary channels fail due to network limitations or technical difficulties. Translation services or multilingual staff contacts should be arranged before traveling to destinations where language barriers might impede critical communications, particularly for handling technical issues, medical emergencies, or security concerns. Addressing these factors before departure ensures you can maintain necessary communication throughout your international journey, especially if contingency plans become necessary due to unforeseen circumstances.
Creating an Optimal International Private Jet Experience
Navigating the complexities of international private jet charter requires thorough preparation, expert guidance, and realistic expectations. The regulatory framework, documentation requirements, customs procedures, and fee structures create a multifaceted landscape that differs significantly from domestic private aviation. Understanding these elements helps establish appropriate budgets, timelines, and contingency plans for successful international travel.
Working with experienced international operators or brokers provides essential expertise in navigating these complexities. Their familiarity with destination-specific requirements, established relationships with foreign service providers, and experience with potential challenges significantly enhances the likelihood of smooth international operations. This expertise justifies the premium typically charged by internationally experienced charter providers compared to primarily domestic operators.
Ultimately, successful international private jet charter requires balancing convenience and luxury with regulatory compliance and operational realities. By understanding the potential pitfalls, hidden costs, and documentation requirements outlined in this guide, you can enjoy the substantial benefits of international private aviation while minimizing disruptions, delays, and unexpected expenses that might otherwise detract from your travel experience.
Permit Application Flowcharts for International Private Jet Operations
Visualizing the International Charter Process
As we've explored the regulatory frameworks, documentation requirements, and operational logistics of international private jet charter, the complexity of these processes becomes evident. To transform this conceptual knowledge into actionable understanding, the following flowcharts provide visual roadmaps for navigating critical procedures. These diagrams distill the multi-step processes discussed-from permit acquisition to documentation timelines-into clear, sequential workflows. Serving as both quick-reference tools and strategic planning aids, they visualize how the operational requirements, fee structures, and compliance considerations interconnect across different flight scenarios. Whether evaluating overflight authorization timelines or preparing for special operations, these flowcharts enable you to anticipate requirements at each stage while maintaining awareness of potential decision points and compliance checkpoints
Standard Overflight Permit Application Process
Securing the right to traverse foreign airspace is fundamental to international private aviation. This flowchart outlines the critical process of obtaining overflight permits, which authorize your aircraft to pass through a nation's sovereign airspace without landing. These permits ensure compliance with national security protocols while establishing your flight's legitimacy with air traffic control systems. The timeline can vary dramatically based on the geopolitical relationships between countries and whether your route crosses restricted or sensitive airspace regions. Expedited processing is available for urgent situations but typically incurs substantial additional fees.
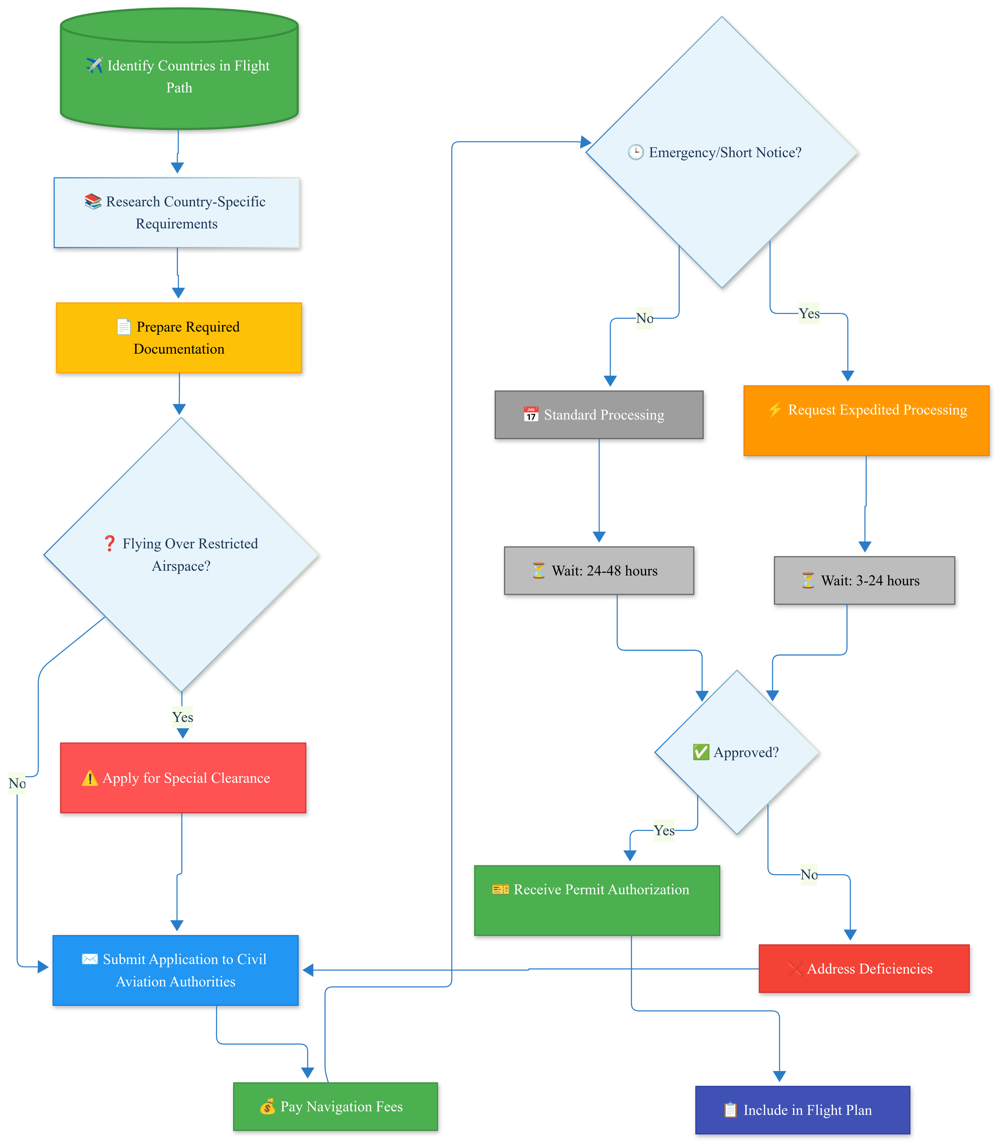
Landing Permit Application Process
Landing permissions represent a critical gateway for international arrivals and are governed by significantly different requirements than domestic operations. This flowchart illustrates the essential steps for securing authorization to land at foreign airports. Note the divergent paths for commercial versus private operations, reflecting the distinct regulatory frameworks applied to each category. The documentation requirements escalate for commercial operations, which face heightened scrutiny regarding insurance coverage, operational specifications, and security protocols. Maintaining compliance with permit conditions throughout your stay is crucial, as violations can impact future permit approvals or even result in monetary penalties.
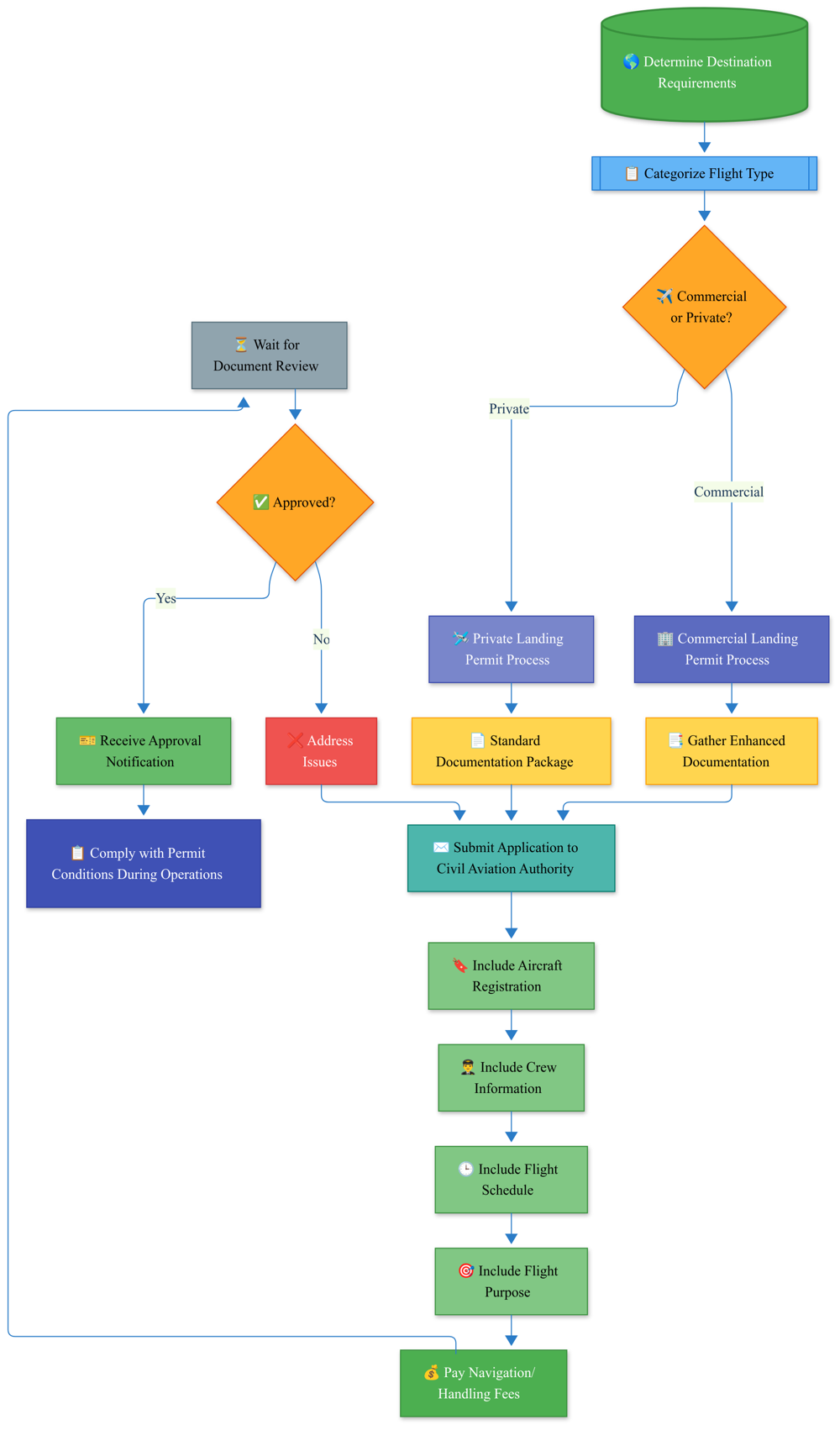
Special Operation Permit Process
Beyond standard flight operations, certain missions require specialized permits that reflect their unique purposes and risk profiles. This flowchart details the process for securing authorizations for diplomatic flights, medical evacuations, hazardous material transport, and other non-standard operations. These specialized permits face enhanced scrutiny due to their sensitive nature, often requiring coordination across multiple government agencies. The timeline varies significantly based on operation type, with medical evacuations typically receiving prioritized processing while diplomatic missions may require ministerial-level approvals. Special operation permits often come with specific operational constraints that must be strictly followed throughout the mission.
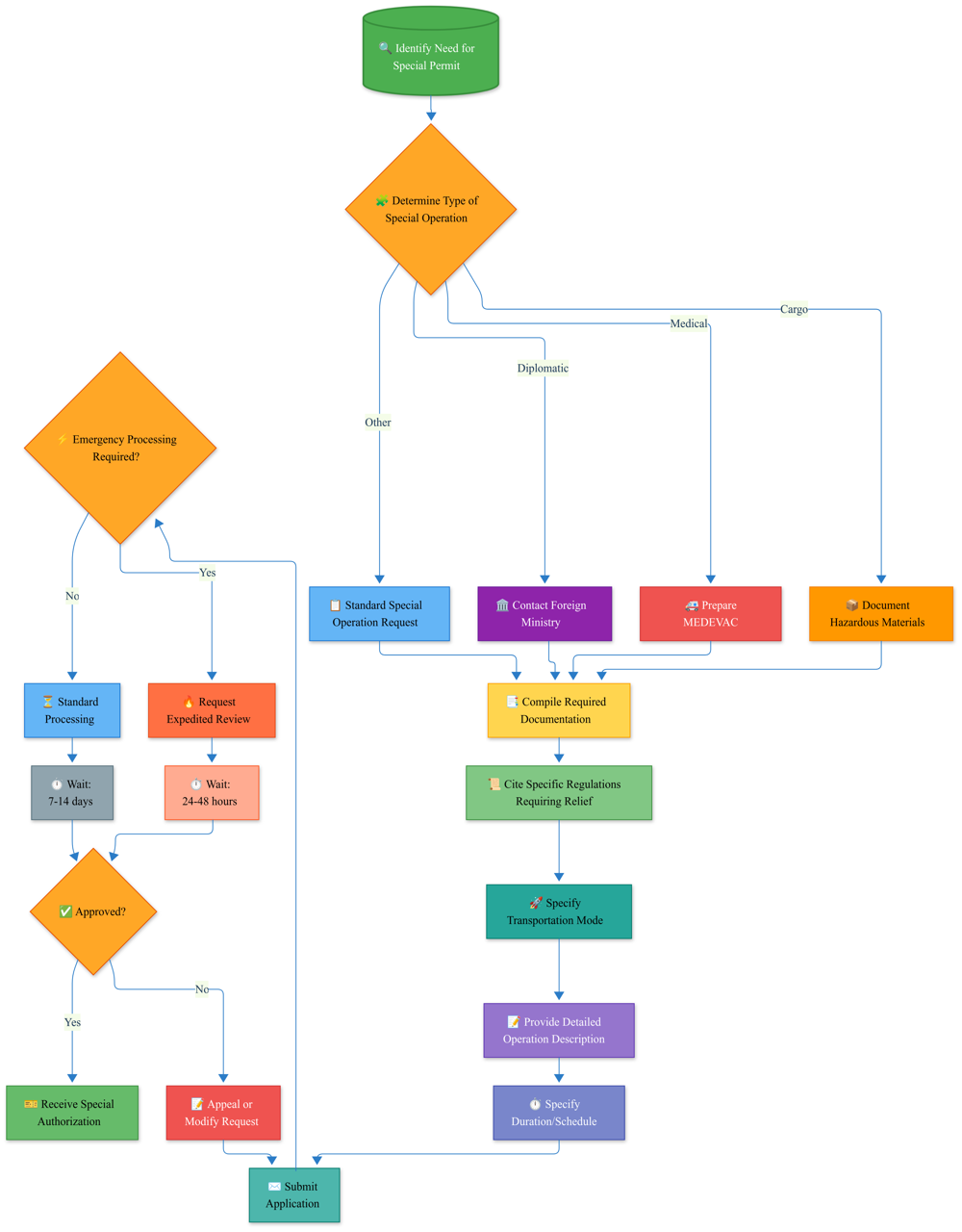
International Documentation Preparation Timeline
Successful international private jet operations depend on meticulous advance planning and documentation preparation. This flowchart presents a comprehensive timeline for preparing international flight documentation, working backward from departure. The extended timeline reflects the complex, interconnected nature of international permit applications, where one document often depends on another being secured first. This sequential approach is essential for avoiding last-minute complications that can ground an aircraft or force schedule changes. Each milestone represents a critical checkpoint in your preparation process, with increasing urgency as departure approaches. Following this structured timeline significantly reduces the risk of documentation-related delays.
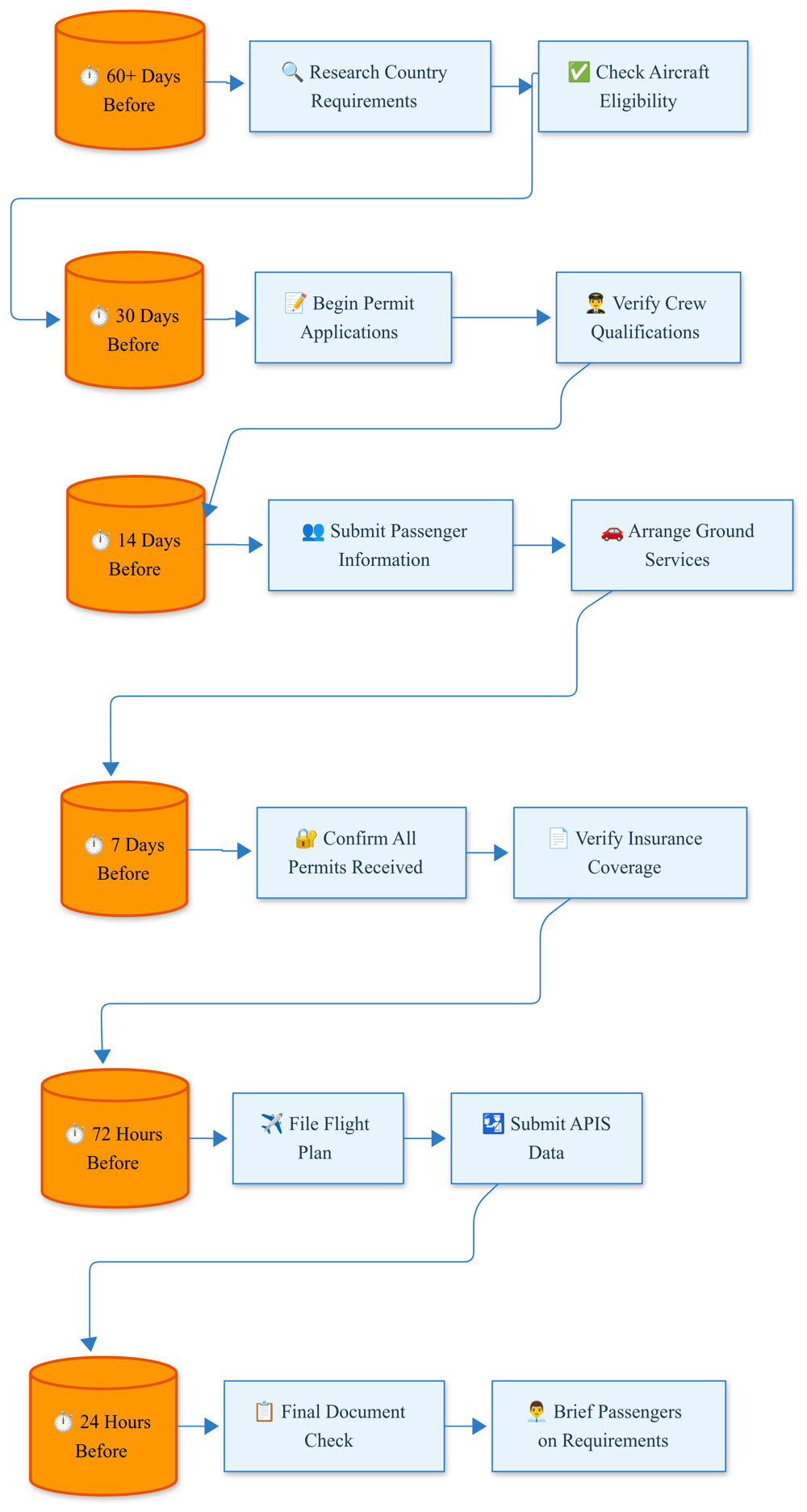
These flowcharts provide a visual guide to navigating the complex permit application processes required for international private jet operations. Working with experienced operators familiar with destination-specific requirements can significantly streamline these processes and help avoid delays or complications.




