The transformation of Shenzhen from a fishing village to China's technology capital has been well documented, but its latest shape shift into a significant force in the global low-altitude economy represents a major development in urban mobility. While cities across the globe work to understand and adapt China's integrated approach to three-dimensional urban mobility, Shenzhen's Qianhai special economic zone has established a leading position in demonstrating how strategic policy innovation, industrial clustering, and cross-border integration can accelerate the commercialization of low-altitude technologies.
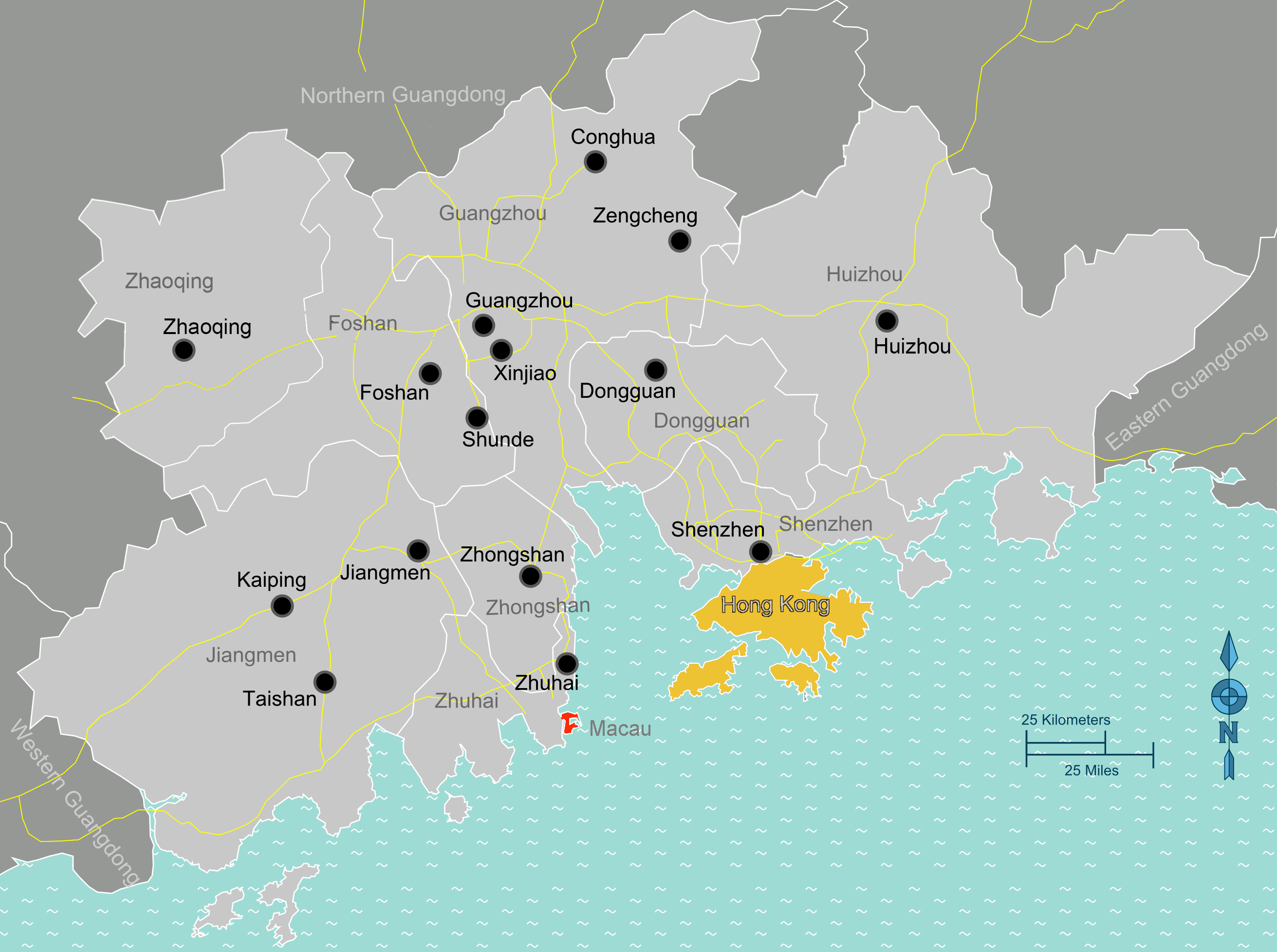
Greater Bay Area encompassing Shenzhen, Hon Kong, Macau and Zhuhai
Shenzhen's low-altitude economy now encompasses an industrial network of over 1,900 enterprises, collectively generating 21.38 billion yuan in value-added output from major industrial enterprises alone, representing a 26.4% year-on-year increase that outpaces most traditional technology industries. Yet beyond these financial metrics lies another indicator of development: operational scale that indicates the commercial viability of low-altitude services.
This operational density represents substantial progress, it demonstrates the performance of network effects that create competitive advantages. While other global regions continue to pursue experimental pilot programs and regulatory sandboxes, Shenzhen has constructed an integrated ecosystem where low-altitude operations have evolved into routine commercial activities embedded within the city's economic fabric.
The Qianhai Innovation Laboratory
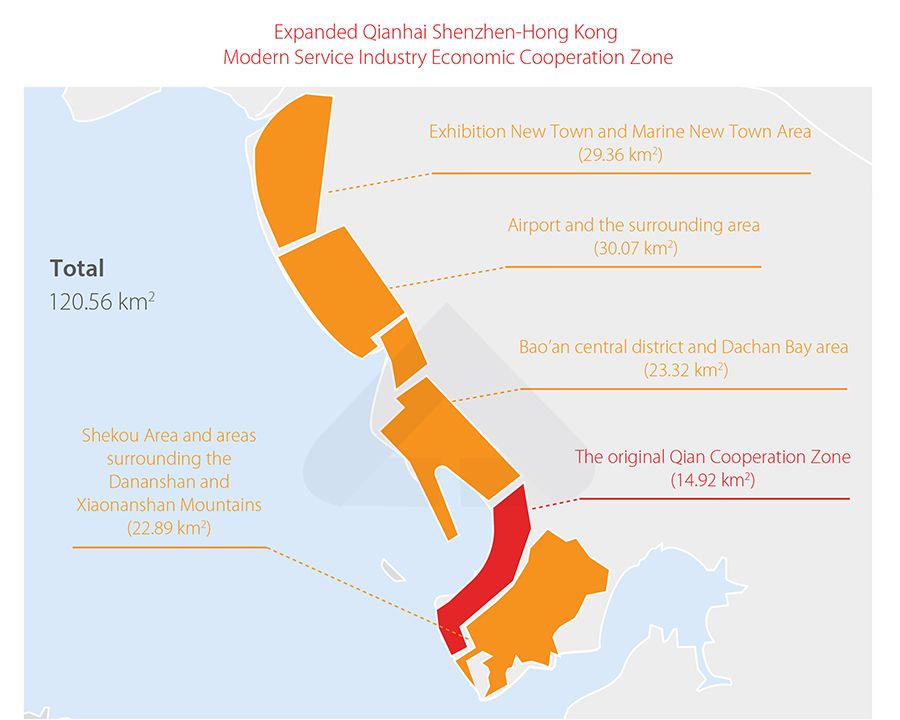
Qianhai special economic zone
The foundation of Shenzhen's development in the low-altitude economy rests on its ability to create policy frameworks that reduce operational friction while maintaining safety standards. The Qianhai special economic zone has emerged as a laboratory for regulatory innovation, establishing a template that other regions worldwide are attempting to replicate with varying degrees of success.
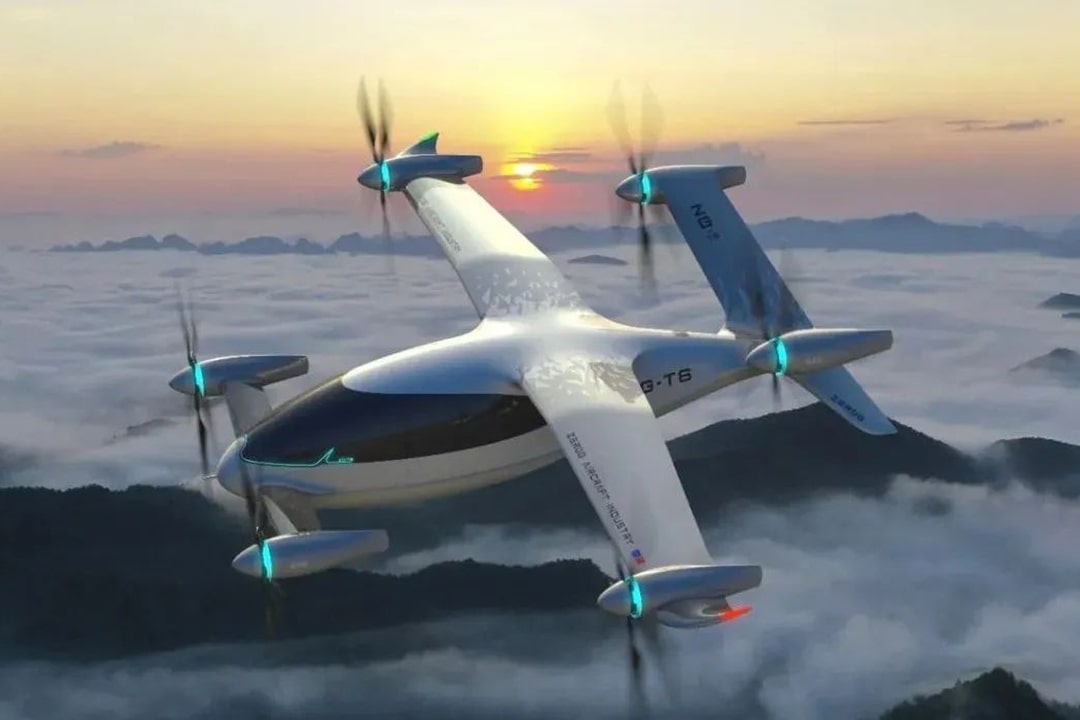

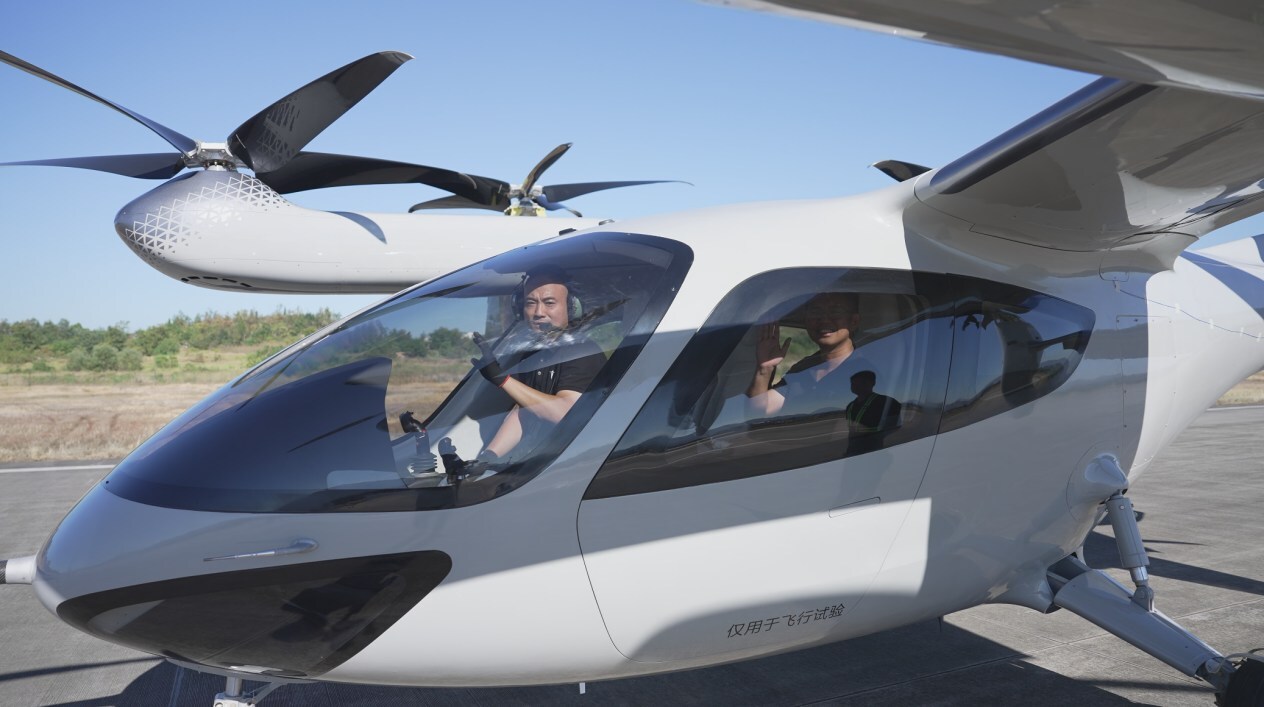
ZG-T6: a six-seat tiltrotor designed as an “air taxi” for urban and intercity travel. It’s ZeroG’s most ambitious model, with market entry projected around 2028.
The zone's approach to enterprise support illustrates the implementation of China's industrial policy framework. Consider the experience of ZeroG Aircraft Industry, an aerospace manufacturer that has benefited from strategic partial upfront funding during complex airworthiness certification processes. This financial approach has allowed the company to navigate the regulatory requirements without depleting their capital reserves. Additionally, ZeroG has exploited dedicated airspace allocation specifically designated for their flight testing operations, providing them with consistent testing environments free from commercial traffic interference.
This combination of targeted financial support and specialized operational resources has enabled ZeroG to accelerate their certification timelines while maintaining safety standards, bringing aircraft designs to market more efficiently than competitors who lack such advantages. This targeted government intervention demonstrates how calibrated support can accelerate technology development timelines, contrasting with the approaches typically adopted in the United States and Europe, where companies must navigate complex regulatory processes with limited and sometime vague government assistance.
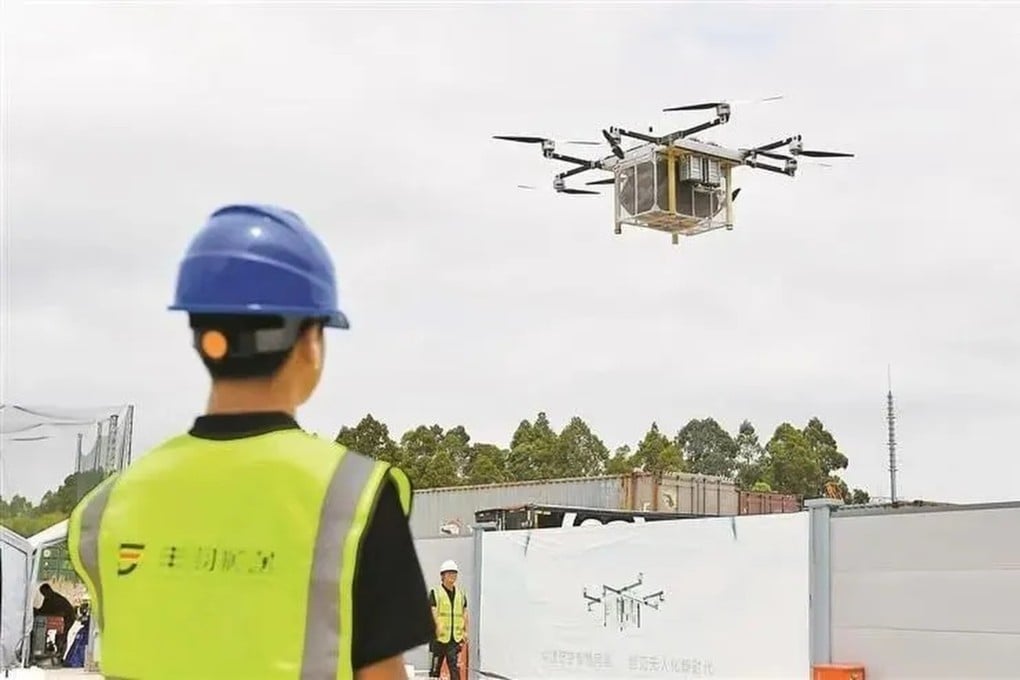

SF Express's subsidiary Shenzhen Fengyi Technology has established a 66-route drone delivery network
SF Express's subsidiary Shenzhen Fengyi Technology has established a comprehensive drone delivery network that now conducts more than 1,000 daily drone flights, carrying over 20,000 parcels across the metropolitan region. This 66-route network spans five major districts—Longgang, Nanshan, Luohu, Longhua, and Pingshan—creating the most extensive urban drone logistics infrastructure currently in operation. Since December 2020, this network has transported 170 tons of cargo through 82,000 individual flights, demonstrating commercial viability at metropolitan scale.
The operational characteristics of this network address one of the complex challenges facing urban low-altitude operations: coordinated traffic management across dense urban areas. Fengyi Technology's intelligent control system provides real-time tracking and route optimization across all 66 routes simultaneously, enabling coordination that traditional logistics companies work to replicate. This level of integration required extensive coordination between municipal authorities, air traffic management systems, and ground-based logistics networks—a coordination challenge that has proven difficult to achieve in other metropolitan areas.
The company's recent capacity expansions along intercity routes show how established networks can scale efficiently. Rather than building isolated pilot projects, the integrated approach allows new routes to leverage existing infrastructure, maintenance capabilities, and operational expertise, creating network effects that reduce costs and increase reliability across the system.
The industrial chain integration cultivated within Qianhai establishes synergistic relationships that transcend individual corporate entities, encompassing technological ecosystems and value networks. Zex Drone Racing's development trajectory demonstrates how the co-location of technological research and development, manufacturing capabilities, scenario application, flight testing, airworthiness services, and exhibition facilities within a single geographic area accelerates innovation cycles while reducing development costs. This clustering effect has attracted leading enterprises from across the low-altitude economy value chain, creating a cycle of investment and innovation that continues to build momentum.
Shenzhen's first-mover advantage in implementing comprehensive low-altitude economy legislation in February 2024 provided regulatory clarity that enabled rapid commercial deployment across the sector. This legislation addressed issues including airspace management protocols, safety standards, and detailed operational procedures that had created uncertainty in other jurisdictions worldwide. This regulatory clarity has proven to be a competitive advantage in attracting investment and fostering enterprise development throughout the Pearl River Delta Greater Bay Area.
Achieving Operational Scale
The achievement of operational scale distinguishes Shenzhen's low-altitude economy from the experimental pilot programs and demonstration projects that characterize development efforts in other global regions. Shenzhen's cargo drones have completed over 780,000 sorties since 2023, establishing the city as a national leader in commercial low-altitude operations.
This flight volume operates across a network of 203 active drone routes and 121 dedicated takeoff and landing points throughout the metropolitan area. The operational density demonstrates commercial viability, with routes spanning diverse urban scenarios including business districts, scenic areas, campuses, and municipal parks. In Shuibei, China's largest gold and jewelry trading center, dedicated drone corridors have reduced traditional 30-minute ground transport times to 12 minutes, enabling secure delivery of high-value cargo.
The network's capability extends beyond urban deliveries to medium-distance logistics operations. Cross-sea routes covering 71.7 kilometers between Shekou and Zhongshan complete deliveries in 45 minutes, demonstrating time-competitive alternatives to traditional transportation for inter-city cargo movement. These operational metrics represent systematic deployment across multiple market segments, from rapid food delivery to Shenzhen Bay Park completed in 10 minutes to specialized transport of valuable commodities.
This scale of operations—nearly 800,000 commercial flights in under two years—establishes benchmarks that other global regions are working to approach. While international operators continue developing regulatory frameworks and conducting trials, Shenzhen has achieved the scale necessary for commercial low-altitude logistics operations.
The integration of low-altitude operations with existing logistics infrastructure represents a capability that other regions continue to work to replicate. Phoenix Wings' strategic position as a subsidiary of SF Express, one of China's largest logistics companies, provides access to established customer relationships, extensive distribution networks, and operational expertise that standalone low-altitude companies typically lack. This integrated operational model has proven challenging to replicate in markets characterized by more fragmented logistics industries and less coordinated business ecosystems.
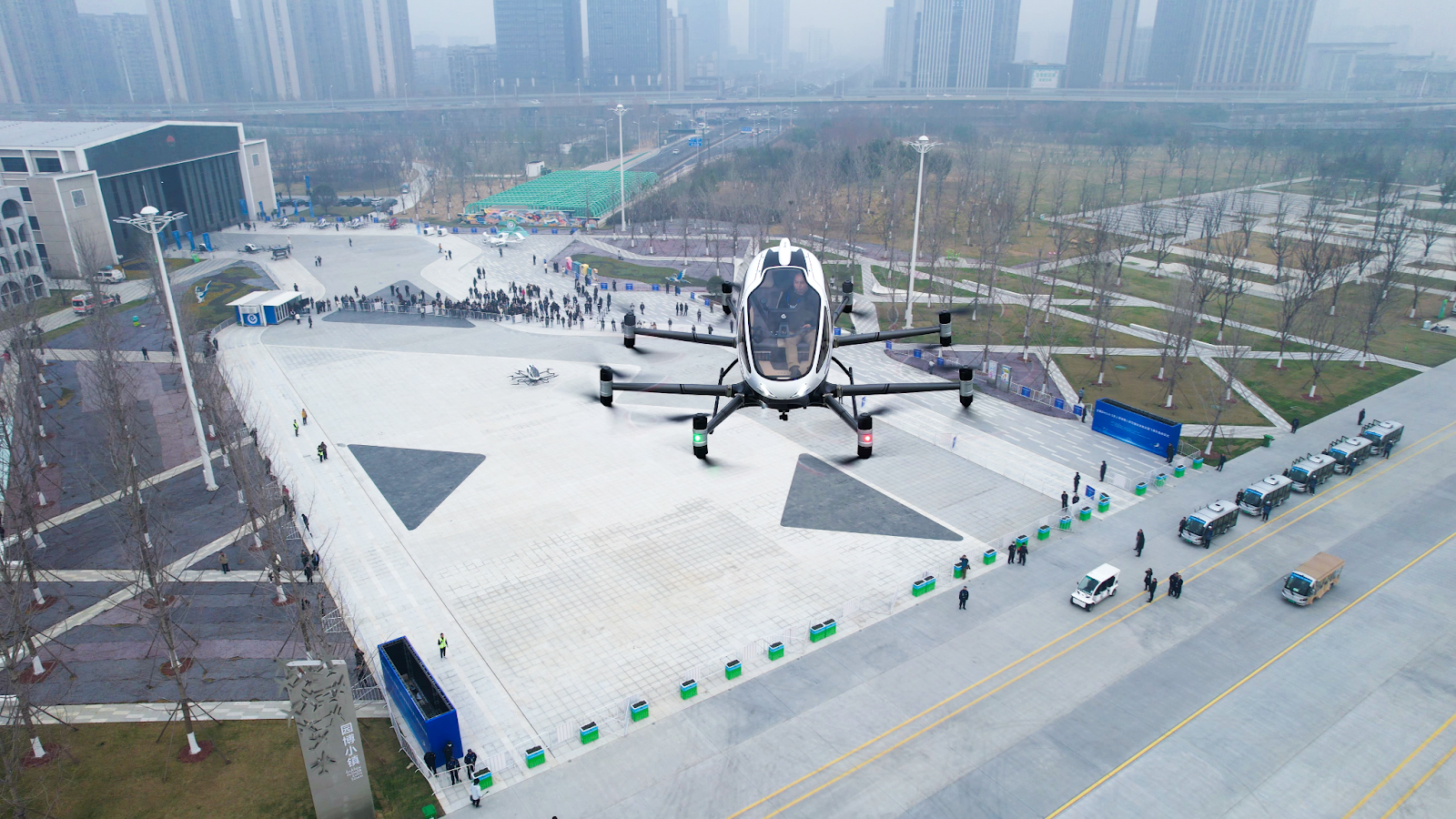

Ehangs EH216-S
The development of autonomous capabilities represents another area where Shenzhen has achieved competitive advantages over international competitors. EHang's achievement of securing the world's first type certificate for an autonomous passenger eVTOL aircraft—the EH216-S—in October 2023 demonstrates Chinese progress in autonomous systems development and regulatory approval processes. This milestone provides Chinese companies with operational capabilities that competitors in other regions are still pursuing through lengthy certification processes that may take years to complete.
The flow of capital into Shenzhen's low-altitude aviation sector signals investor confidence. XPeng AeroHT closed a US $150 million (≈ 1.1 billion yuan) Series A round led by IDG Capital and 5Y Capital in late 2023. Public filings and press releases show cumulative external funding of roughly US $500 million (≈ 3.6 billion yuan) since 2021.
XPeng AeroHT's **** a subsidiary of electric vehicle manufacturer XPeng Motors, has established manufacturing facilities in Guangzhou while maintaining research and development operations in Shenzhen. Their flagship X2 aircraft, a two-seat eVTOL designed for urban air mobility, has completed over 15,000 test flights across multiple development phases.
The company's certification strategy focuses on both domestic and international markets, pursuing airworthiness certification through China's CAAC while simultaneously engaging with European and U.S. regulatory authorities. XPeng AeroHT's X3 model, currently in development, targets commercial passenger operations with enhanced safety systems and autonomous flight capabilities.
Shenzhen's broader low-altitude ecosystem continues to attract significant public and private investment, with XPeng AeroHT's capital base measured in the low-single-billion-yuan range. This level of funding is substantial for an early-stage eVTOL developer yet remains comparable to peers in the United States and Europe, reflecting the global nature of competition in urban air mobility markets.
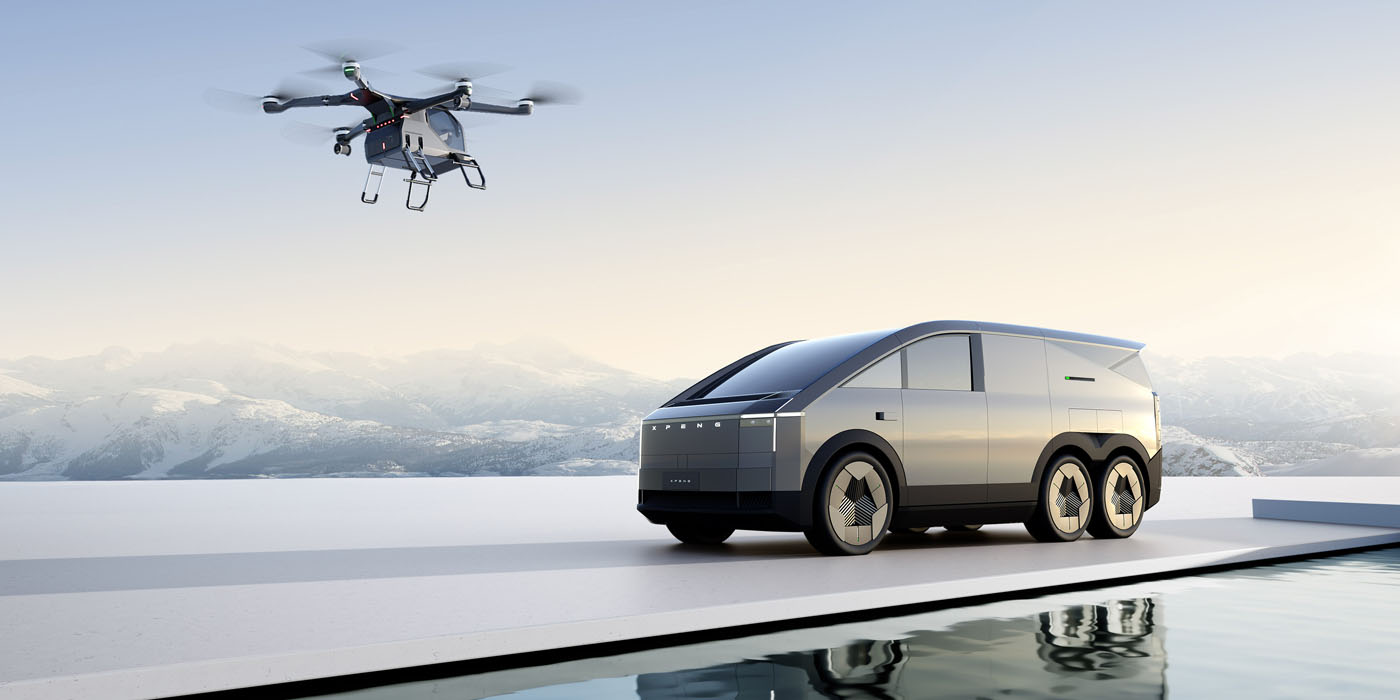

XPeng AeroHT's modular flying car
China’s approach to Safety Framework and Risk Management
The rapid scaling of Shenzhen's low-altitude operations raises essential questions about safety management and risk mitigation in autonomous aircraft operations over populated areas. Analysis of the city's safety framework reveals both sophisticated regulatory approaches and significant challenges in transparency and oversight that affect international confidence in the sector's long-term sustainability.
The scale of operations in Shenzhen provides substantial data for safety analysis, though access to comprehensive information remains limited. China's 780,000+ commercial flights and 1.88 million registered drones represent the world's largest dataset for low-altitude commercial operations, yet most safety information originates from company disclosures rather than centralized regulatory databases.
EHang's safety record illustrates both the achievements and transparency challenges facing the sector. The company reports over 50,000 flights with zero passenger fatalities, while acknowledging "early testing incidents" during development phases. However, detailed incident data and investigation reports remain largely unavailable for independent verification.
Phoenix Wings operations through SF Express provide more comprehensive flight hour documentation, with minimal publicly disclosed incidents across their 66-route network. The company's integration with existing logistics infrastructure may contribute to operational safety through established maintenance and operational procedures, though independent safety audits are not publicly available.
International context reveals mixed comparative performance. The European Union Aviation Safety Agency reported one fatality and one serious injury from drone operations in 2023, while research projections suggest major cities could experience 38.35 crashes and 7.51 takeoff/landing accidents annually at 0.5% logistics market penetration. Traditional aviation maintains a global accident rate of 1.87 accidents per million departures according to ICAO data, providing baseline context for emerging low-altitude operations.
Regulatory Framework and Standards
China's safety management approach centers on the CAAC CCAR-92 regulations, which establish comprehensive frameworks for unmanned aircraft safety management. This regulatory structure creates a three-tier operational classification system distinguishing between Open, Specific, and Certified categories based on risk profiles and operational complexity.
Certification standards demonstrated through EHang's type certificate process indicate rigorous technical requirements, though the specific criteria and testing protocols differ from international standards developed by EASA and the FAA. These differences create challenges for international operations and regulatory mutual recognition agreements.
Technology-enhanced safety features including redundancy systems, fail-safe design principles, and autonomous safety capabilities represent significant advances in aircraft reliability. However, the integration of diverse aircraft types and systems within unified safety frameworks creates complexity that strains oversight capabilities during periods of rapid sector growth.
Air Traffic Integration Challenges
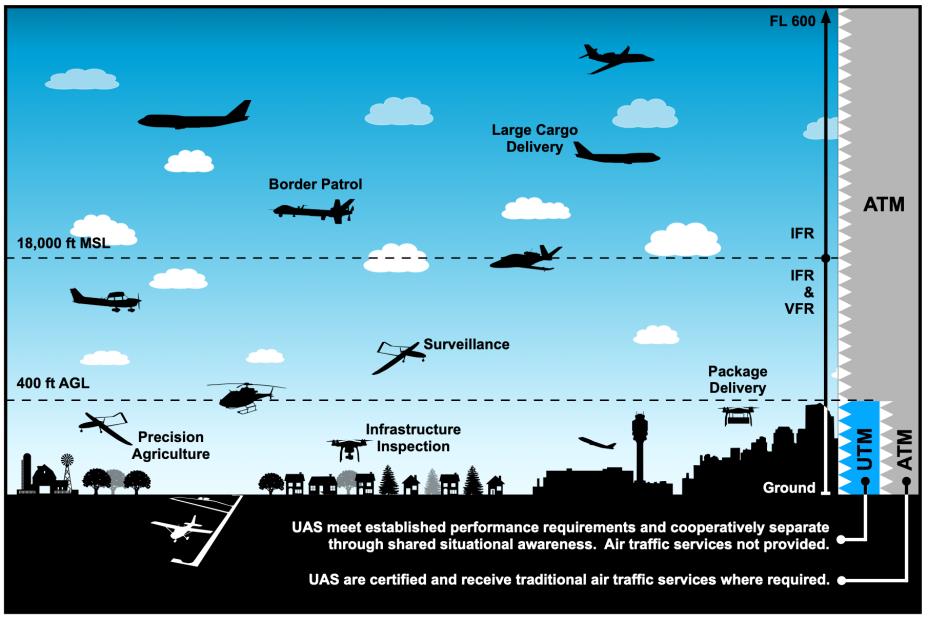
The UTM (Unmanned Traffic Management) system architecture
The management of low-altitude airspace presents unique challenges distinct from traditional aviation safety frameworks. Shenzhen's hierarchical airspace system distinguishes between controlled, restricted, and unrestricted zones, enabling differentiated safety protocols based on operational environments and risk profiles.
Digital airspace management utilizing 3D modeling, dynamic route planning, and automated conflict detection represents advanced approaches to traffic coordination. The UTM (Unmanned Traffic Management) system architecture enables centralized coordination with distributed operations, though the effectiveness of these systems during emergency conditions requires further validation.
Separation standards from traditional aviation include vertical, horizontal, and temporal protocols designed to prevent conflicts with manned aircraft. However, the operational complexity increases significantly in urban environments where multiple altitude layers and flight corridors must coordinate with existing helicopter operations, emergency services, and potential future urban air mobility services.
Emergency Response and Risk Mitigation
China has developed multi-level emergency response systems encompassing aircraft-level, operator-level, regional, and national frameworks. These systems include specialized technical response teams, medical emergency protocols, fire and rescue capabilities, and security response procedures tailored to low-altitude operations.
Risk assessment methodologies employ systematic hazard identification and mitigation strategies, though the rapid pace of operational scaling creates challenges for comprehensive risk evaluation. The 34% annual growth in drone registrations strains oversight capabilities and creates potential gaps in safety monitoring systems.
Post-incident procedures include recovery operations and investigation protocols designed to integrate lessons learned into operational improvements. However, public access to detailed investigation reports remains limited, reducing opportunities for industry-wide learning and international confidence building.
Insurance and Liability Frameworks
The development of insurance markets for low-altitude operations indicates growing sector maturity, with Swiss Re projecting an RMB 8-10 billion market by 2035. Insurance products now include hull coverage, third-party liability, personal accident, carrier's liability, and professional liability insurance specifically designed for drone operations.
China Re and CPIC collaboration in developing specialized third-party liability insurance demonstrates institutional support for sector development, though premium structures and coverage limits reflect the evolving understanding of operational risks. Risk assessment methodologies for low-altitude operations continue developing as operational data accumulates.
Regulatory Oversight Evolution
The establishment of CAAC's new Steering Group for General Aviation and Low-Altitude Economy in July 2025 indicates institutional recognition of oversight challenges and coordination needs. This structure aims to improve certification processes, operator oversight, and continued airworthiness monitoring.
Real-time monitoring capabilities through mandatory transponders, centralized tracking systems, and automated alert mechanisms provide enhanced situational awareness compared to traditional general aviation. However, the integration of these systems with existing air traffic control infrastructure requires continued development and international coordination.
International regulatory coordination through ICAO participation and bilateral agreements faces challenges due to differences in certification standards, operational approaches, and transparency requirements between Chinese and international regulatory frameworks.
Critical Assessment: Transparency and Oversight Challenges
While China's safety framework demonstrates sophisticated approaches to risk management, significant limitations affect international confidence and independent verification capabilities:
Data transparency challenges persist across multiple areas. Most safety information originates from company disclosures rather than comprehensive regulatory databases. No centralized incident reporting system comparable to international standards exists, limiting opportunities for systematic safety analysis and improvement.
Investigation transparency remains constrained, with limited public access to detailed incident reports that could inform international best practices and regulatory development. This opacity creates challenges for regulatory authorities in other regions considering similar operational approaches.
Scale and complexity management presents ongoing challenges as rapid growth strains oversight capabilities. Operating over densely populated urban areas creates unique risk profiles requiring specialized mitigation approaches that continue evolving as operational experience accumulates.
Implications for Low Altitude Economy Development
The analysis reveals that while China has developed sophisticated safety frameworks enabling large-scale commercial operations, significant challenges remain in building international confidence through enhanced transparency and standardized reporting. The safety record appears positive based on available data, though the lack of comprehensive public reporting systems limits independent verification and international regulatory coordination.
These transparency limitations may affect the sector's international expansion potential and create challenges for establishing mutual recognition agreements with other regulatory authorities. Addressing these gaps through enhanced data sharing and standardized reporting could strengthen both domestic oversight capabilities and international confidence in China's low-altitude economy development model.
China's approach to community acceptance of low-altitude economy

China's approach to community acceptance of low-altitude economy development reflects characteristics of the country's governance system, emphasizing coordinated implementation, benefit communication, and integration with existing development priorities. This approach has enabled deployment of low-altitude services while maintaining public acceptance levels, though it operates within a political and cultural context that presents both advantages and limitations for replication in other regions .
Integration with Urban Development Frameworks
The integration of low-altitude economy development with broader smart city initiatives in Chinese urban areas has positioned these technologies as components of modernization rather than standalone technological additions. Cities like Shenzhen have framed low-altitude services as extensions of their technology development strategies, creating narratives that connect individual services to broader community benefits and national development objectives .
This integration approach offers coordination advantages by aligning low-altitude services with existing infrastructure planning and public investment priorities. However, it also creates dependency relationships where community acceptance becomes tied to broader political and economic development narratives that may not translate to different governance contexts.
Practical Benefits Focus
The emphasis on practical benefits and service delivery in China's approach to community engagement directs public attention toward tangible advantages of low-altitude services rather than regulatory or privacy concerns. Phoenix Wings' drone delivery operations have demonstrated time savings and convenience benefits, building public support through immediate, observable advantages for users and observers .
While this results-oriented approach can effectively demonstrate value propositions, it may also limit discussion of longer-term considerations such as privacy implications, environmental impact, or employment effects that concern communities in other regions.
Institutional Coordination Mechanisms
The coordination between government agencies, technology companies, and community organizations in China creates channels for addressing public concerns through established institutional processes rather than adversarial engagement. This coordination enables response to community issues and development of solutions that balance operational requirements with public concerns, though this approach depends on high levels of institutional trust that varies significantly across different political contexts .
This institutional integration can facilitate rapid problem-solving and conflict resolution, but may also reduce opportunities for independent community advocacy and alternative perspective development that characterize democratic consultation processes.
Cultural and Social Context Factors

The acceptance of technological innovation in Chinese urban areas provides a supportive environment for low-altitude economy development that may differ from communities with different cultural attitudes toward technology adoption. The adoption patterns of mobile payment systems, ride-sharing services, and other technological innovations in China indicate general openness to new technologies that extends to low-altitude services .
However, this cultural receptivity to technology adoption may reflect specific historical, economic, and social conditions that are not necessarily reproducible in communities with different experiences with technological change, privacy expectations, or governance relationships.
Scale and Implementation Dynamics
The scale and speed of implementation in China creates momentum through demonstrated success and widespread adoption. The achievement of operational scale in cities like Shenzhen provides evidence that low-altitude services can operate safely and beneficially, addressing concerns that might persist in smaller-scale implementations. This approach requires substantial initial investment and coordination but can facilitate community acceptance once operational thresholds are reached .
While rapid scaling can demonstrate viability and build confidence, it may also limit opportunities for iterative community feedback, gradual adaptation, and the development of locally-appropriate operational models that might emerge through more incremental deployment approaches.
Parallel Implications
China's state-directed strategy for gaining public support demonstrates both benefits and constraints that other areas should consider when developing their own low-altitude economic frameworks.
Coordination Benefits:
- Unified messaging and benefit communication
- Rapid deployment capabilities
- Integrated planning processes
Replication Challenges:
- Dependence on high institutional trust levels
- Limited independent community input mechanisms
- Cultural context requirements for technology acceptance
Understanding these dynamics proves essential for regions seeking to develop effective community engagement strategies appropriate to their specific governance structures, cultural contexts, and stakeholder expectations.
Global Replication Initiatives: Challenges and Constraints
The development of Shenzhen's low-altitude economy has prompted governments and metropolitan regions worldwide to develop strategies for low-altitude economic development within their own jurisdictions. However, attempts to replicate China's coordinated approach have revealed the challenges of implementing comprehensive low-altitude economic strategies within different political, economic, and regulatory contexts.
United States: Market Forces and Regulatory Complexity
The fragmented nature of U.S. regulatory authority has created challenges for coordinated development efforts. The Federal Aviation Administration maintains primary authority over airspace management and aircraft certification processes, while state and local governments control aspects including land use planning, zoning regulations, and infrastructure development. This division of authority has complicated efforts to develop comprehensive low-altitude economic strategies and has resulted in a patchwork of local initiatives with limited coordination mechanisms.
Technological Achievements and Regulatory Progress
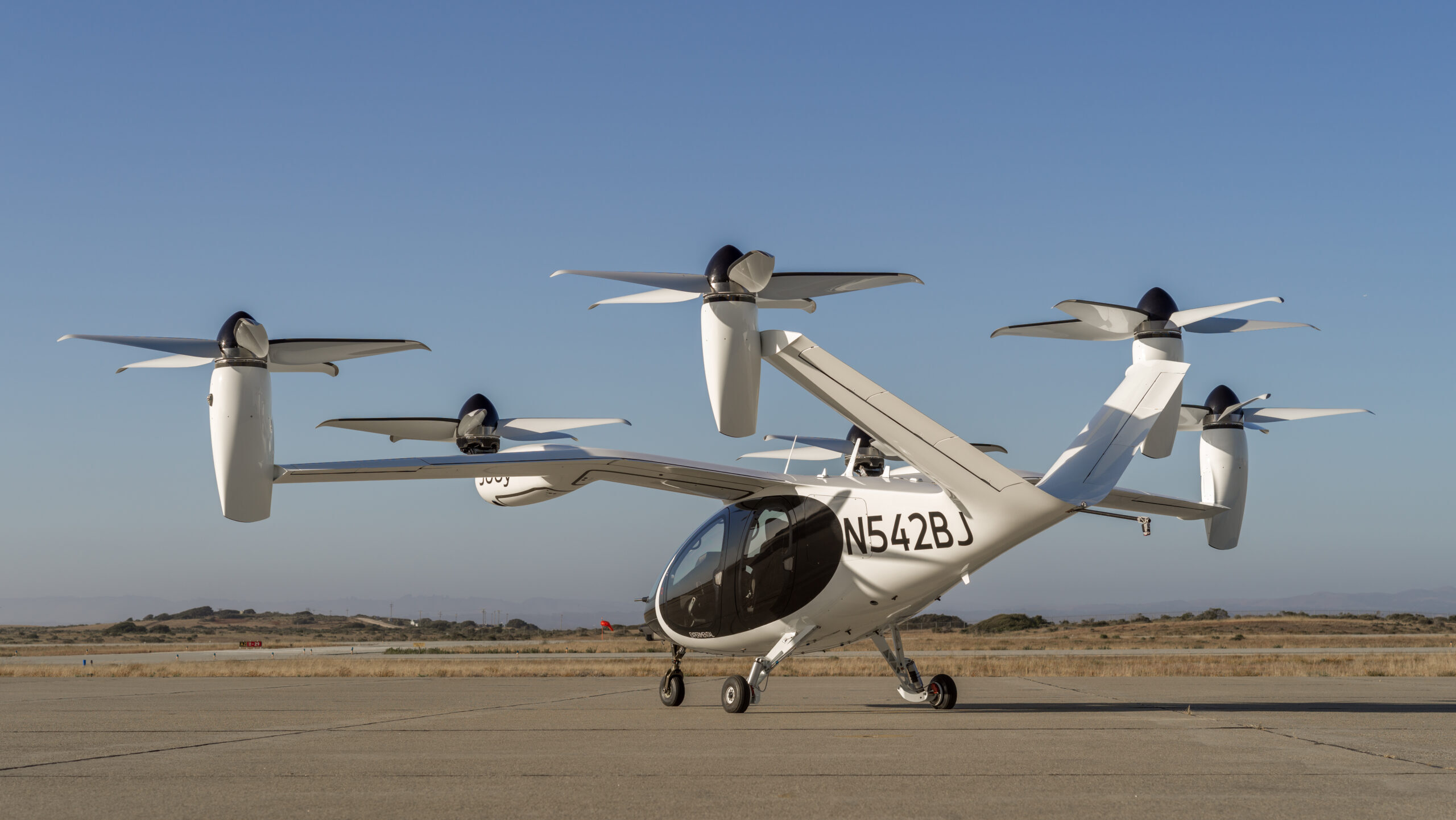

Joby Aviation eVTOL aircraft
The United States' approach to advanced aerial mobility has achieved notable technological milestones in recent years, with companies like Joby Aviation demonstrating electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) capabilities through extensive flight testing programs and certification progress. Simultaneously, technology companies such as Amazon have implemented operational drone delivery services in markets including Arizona, where customers receive packages via unmanned aerial vehicles.
These achievements highlight America's continued leadership in aerospace innovation and technical development. However, the scaling and widespread deployment of these technologies has proceeded at a different pace than comparable initiatives in China, reflecting both the regulatory framework maintained by the Federal Aviation Administration and the challenges of coordinating complex airspace integration across multiple federal, state, and local jurisdictions.
This measured pace also stems from the necessity of balancing diverse stakeholder interests—including privacy advocates, traditional aviation operators, local communities, and commercial entities—each with competing priorities and concerns regarding safety, noise, privacy, and economic impact. While this deliberative approach may extend implementation timelines, it potentially ensures more sustainable and socially acceptable integration of these aerial technologies into American society.
Accelerating Vertiport Infrastructure Development
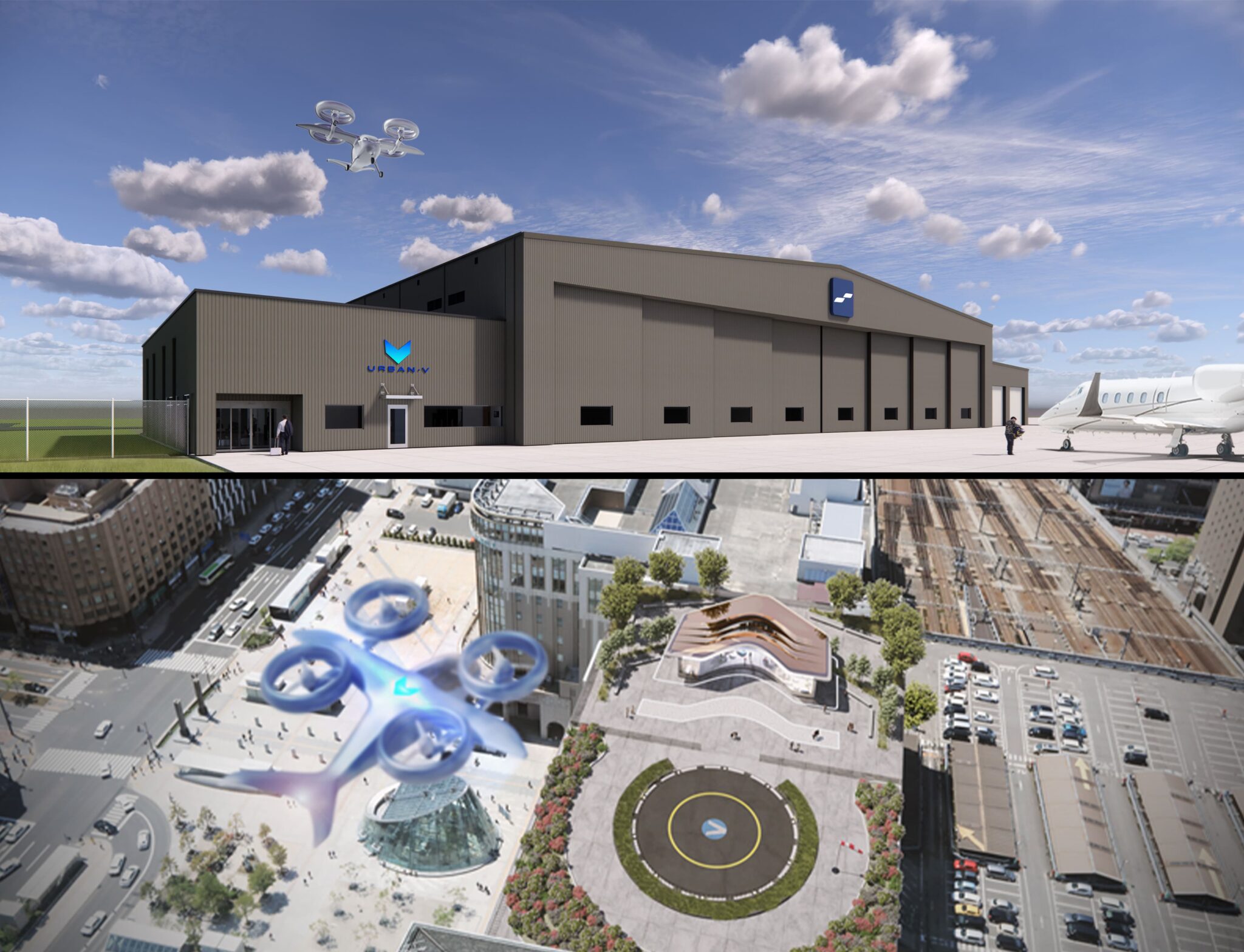

UrbanV and Signature Aviation targets vertiport networks across Florida, New York, California, and Texas
Despite regulatory fragmentation, vertiport development has accelerated significantly across the United States in 2025, with 92 U.S. cities and airports maintaining active plans for eVTOL operations. This infrastructure development represents a critical foundation for the sector's commercial deployment, addressing the "chicken-and-egg" problem of needing operational infrastructure before aircraft certification completion.
State-Level Legislative Support has emerged as a key driver, exemplified by Florida's Senate Bill 1662, which took effect July 1, 2025. This legislation authorizes the Florida Department of Transportation to fund up to 100 percent of vertiport project costs for capital improvements, while expanding the statutory definition of "airport" to explicitly include vertiports and vertistops. The law demonstrates how state governments can provide regulatory clarity and financial support despite federal oversight complexities.
Private Sector Partnerships are scaling vertiport development through strategic alliances. The June 2025 joint venture between UrbanV and Signature Aviation targets vertiport networks across Florida, New York, California, and Texas, leveraging Signature's existing network of 200+ private aviation terminals. This partnership approach enables rapid infrastructure deployment by utilizing existing aviation facilities and regulatory relationships.
US Major Urban Market Preparation
New York City leads in urban vertiport development, with the Economic Development Corporation unveiling a "Downtown Skyport" at the Manhattan heliport in April 2025—the city's first hub specifically designated for eVTOL air taxis. Multiple operators including Blade (partnering with Beta Technologies) and United Airlines (partnering with Archer Aviation) have announced plans for early air-taxi services in NYC.
Miami has become a priority market for multiple eVTOL developers, with Joby Aviation, Archer Aviation, Eve Air Mobility, and Hyundai's Supernal all targeting the region for initial operations. Archer Aviation's partnership with Reef, which owns approximately 4,500 parking garages across the U.S., enables vertiport construction atop existing parking structures in both Los Angeles and Miami.
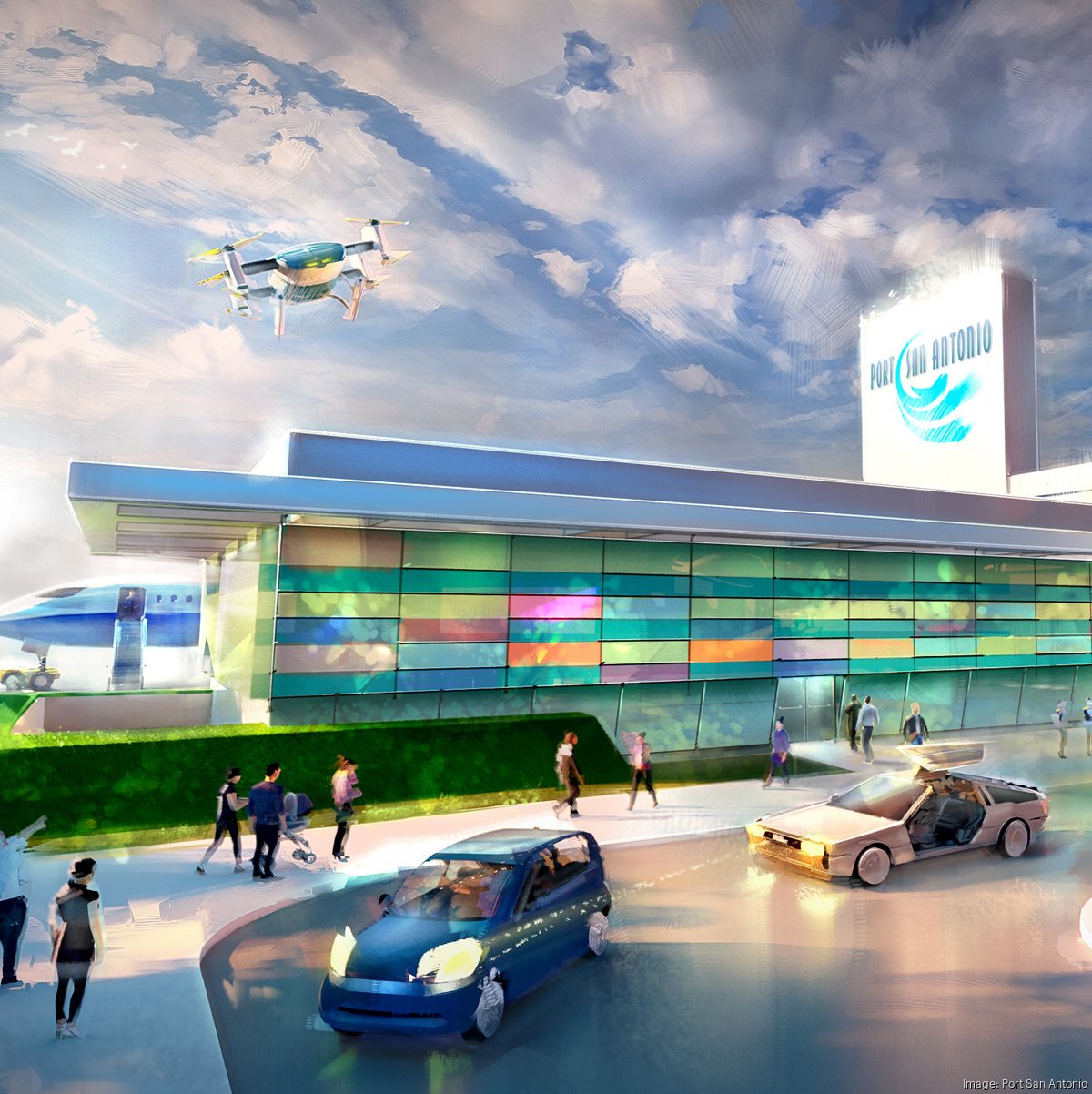

Port San Antonio's vertiport development
Texas presents unique opportunities through projects like Port San Antonio's vertiport development, part of a $100 million airfield renovation that could produce "the country's first purpose-built vertiport". The project includes landing pads, charging infrastructure, and integration with the port's 1,900-acre campus that provides controlled airspace for testing operations.
The FAA forecasts operational debut of electric air taxis by 2028, though vertiport infrastructure development suggests readiness for earlier deployment once aircraft certifications are completed. This infrastructure-first approach may enable more rapid scaling once regulatory approvals are secured, contrasting with development models that require simultaneous aircraft and infrastructure deployment.
European Union: Regulatory Leadership with Implementation Challenges
The European Union has positioned itself as a leader in developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks for low-altitude operations, with particular emphasis on environmental sustainability and safety standards. The European Union Aviation Safety Agency has developed detailed regulations for unmanned aircraft systems and continues working on certification standards for eVTOL aircraft.
European companies like Lilium and Volocopter have achieved technological milestones and attracted investment capital. However, the European approach has been characterized by longer development timelines and more conservative operational deployment strategies compared to China's rapid scaling methodology.
The EU's strong emphasis on environmental sustainability has created opportunities for companies that can demonstrate superior environmental performance, but has simultaneously created additional regulatory requirements that can slow commercial deployment. The focus on noise reduction and emissions standards reflects important European priorities but may create trade-offs in terms of operational flexibility and cost management.
EU Major Urban Market Preparation
European cities have accelerated infrastructure planning and regulatory preparation for eVTOL operations, with multiple metropolitan areas advancing comprehensive urban air mobility strategies despite the EU's traditionally conservative deployment approach.

Paris Re.Invent Air Mobility
Paris leads European urban air mobility preparation through its ambitious "Re.Invent Air Mobility" initiative. The Paris Region has designated multiple vertiport locations across the metropolitan area, including sites at Charles de Gaulle Airport, Orly Airport, and urban locations such as the Pont de Sèvres heliport. Groupe ADP (Aéroports de Paris) has partnered with VoloCity to develop vertiport infrastructure, targeting initial passenger services for the 2024 Olympics legacy operations. The city's integrated approach combines vertiport development with existing public transit systems, positioning air taxis as premium components within multimodal transportation networks.
Amsterdam has emerged as a testing ground for European regulatory frameworks through its "Amsterdam Urban Air Mobility" program. The Netherlands' centralized aviation authority enables coordinated development between Schiphol Airport, the city government, and technology companies including Lilium and PAL-V. The Dutch approach emphasizes environmental integration, with vertiport designs required to meet stringent noise reduction and carbon neutrality standards. KLM's partnership with various eVTOL developers positions Amsterdam as a hub for both passenger and cargo urban air mobility services.
Munich leverages Germany's strong aerospace industry through BMW Group's venture into urban air mobility and partnerships with Lilium. The Bavarian state government has designated Munich as a priority region for eVTOL testing and certification, with planned vertiport locations at Munich Airport and urban sites in the city center. The integration with existing S-Bahn and U-Bahn systems reflects German preferences for comprehensive transportation planning rather than standalone air mobility solutions.
London maintains active urban air mobility development despite Brexit complications affecting EU regulatory harmonization. The Civil Aviation Authority has established specific frameworks for eVTOL operations, while Transport for London has identified potential vertiport locations at Battersea, London City Airport, and Thames-adjacent sites. Partnerships between Rolls-Royce, BAE Systems, and international eVTOL developers position London as a bridge between European and global urban air mobility markets.
Milan has integrated urban air mobility planning with its broader smart city initiatives, designating vertiport locations that connect with high-speed rail terminals and existing helicopter infrastructure. The Lombardy region's support for aerospace development, combined with Italy's growing role in European aviation policy, positions Milan as a southern European hub for eVTOL operations.
Stockholm represents Nordic approaches to urban air mobility through its emphasis on environmental sustainability and digital infrastructure integration. Sweden's regulatory framework for autonomous systems provides advantages for eVTOL certification, while Stockholm's existing congestion pricing and environmental zones create market conditions favorable to premium air mobility services.
The coordination between these metropolitan areas reflects broader European Union efforts to harmonize urban air mobility standards while allowing regional flexibility in implementation approaches. However, the complexity of coordinating across multiple national regulatory frameworks continues to create longer development timelines compared to more centralized governance systems.
Singapore and UAE: City-State Advantages and Strategic Positioning
Singapore and the United Arab Emirates have emerged as players in low-altitude economy development, leveraging their advantages as city-states with centralized authority and strategic geographic positions. Both countries have implemented strategies that combine government support with private sector development.
Singapore's approach has focused on developing capabilities for urban air mobility and drone delivery services, with particular emphasis on integration with the country's smart city initiatives. The government has established regulatory sandboxes and provided support for technology development and testing.
The UAE has positioned itself as a regional hub for low-altitude economy development, with Dubai announcing plans for autonomous air taxi services and cargo delivery operations. The country's centralized authority and willingness to embrace new technologies have enabled progress in regulatory framework development and operational deployment.
However, both Singapore and the UAE face limitations in terms of market size and geographic scope that constrain their ability to achieve the scale advantages demonstrated in China. Their strategies focus on becoming regional hubs and technology leaders rather than developing comprehensive domestic markets.
Japan and South Korea: Technology Leadership and Market Development
Japan and South Korea have leveraged their technological capabilities and manufacturing expertise to develop positions in low-altitude economy technologies. Both countries have strong aerospace industries and advanced manufacturing capabilities that provide foundations for low-altitude economy development.
Japan's approach has emphasized the development of autonomous systems and integration with existing transportation infrastructure. The country's aging population and geographic characteristics create natural applications for low-altitude solutions, particularly in rural areas and for emergency services.
South Korea has focused on developing advanced air traffic management systems and integration with 5G communication networks. The country's technological capabilities in telecommunications and electronics provide advantages in developing the digital infrastructure required for large-scale low-altitude operations.
Japanese Manufacturing Leadership and SkyDrive Development
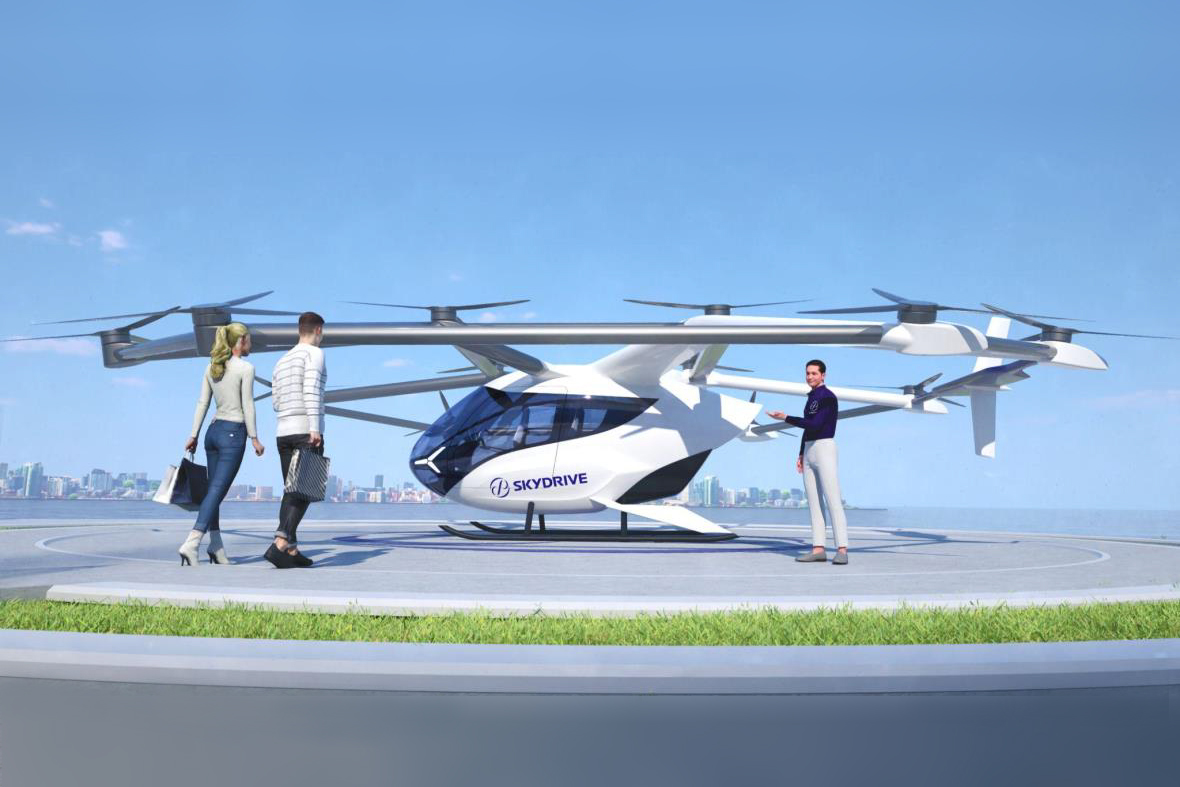

SkyDrive's SD-05 aircraft,
SkyDrive Inc. represents Japan's most advanced eVTOL development program, having achieved significant milestones in autonomous passenger aircraft development. The company completed Japan's first manned eVTOL flight in 2020 and has since progressed through multiple certification phases with the Japan Civil Aviation Bureau (JCAB). SkyDrive's SD-05 aircraft, designed for urban air mobility applications, features a compact design optimized for Japanese urban environments and regulatory requirements.
Manufacturing partnerships demonstrate Japan's integrated approach to low-altitude economy development. Toyota Motor Corporation's investment in SkyDrive reflects automotive industry recognition of urban air mobility potential, leveraging Toyota's expertise in electric powertrains and autonomous systems. Suzuki Motor's collaboration on lightweight aircraft components and Panasonic's contribution of battery systems illustrate the cross-industry coordination characterizing Japan's development model.
Infrastructure development focuses on integration with existing transportation networks. Osaka Bay Area has been designated as a priority region for eVTOL operations, with planned vertiports at Kansai International Airport, Osaka Port, and multiple urban locations connected to existing rail networks. The 2025 Osaka Expo serves as a target timeline for initial commercial passenger services, though regulatory approval timelines may extend deployment schedules.
Japanese regulatory approach emphasizes safety validation and systematic testing protocols. The Japan Civil Aviation Bureau's certification framework requires extensive flight testing and safety validation, reflecting Japanese cultural preferences for thorough evaluation before commercial deployment. This approach contrasts with more accelerated certification processes in other regions but aims to ensure public confidence in safety standards.
South Korean Advanced Air Mobility Programs
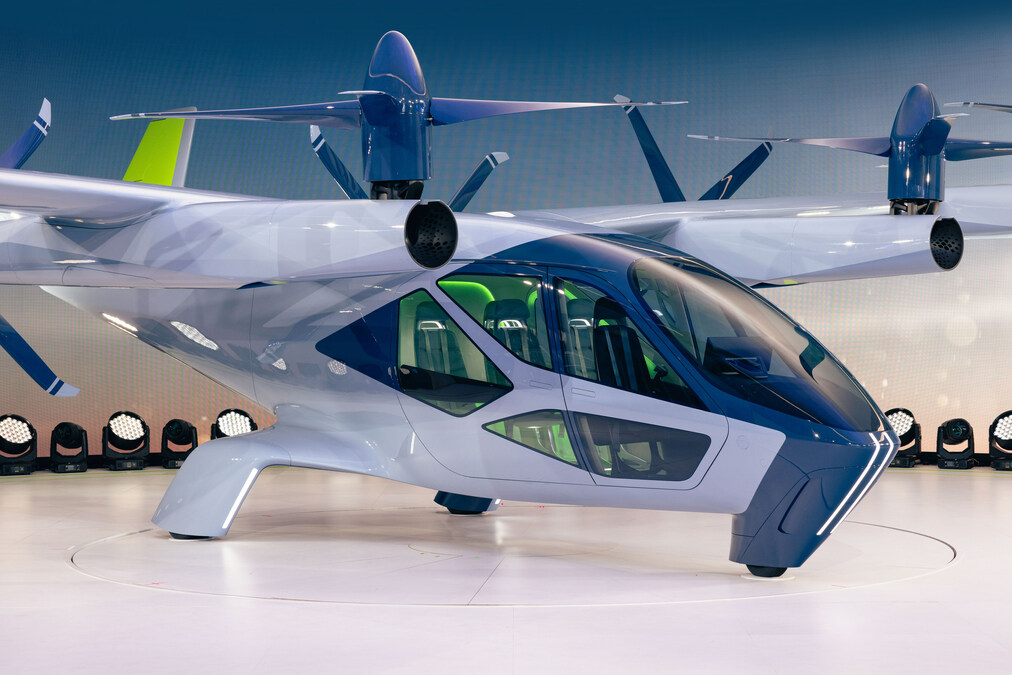

Hyundai S-A2 aircraft
Hyundai Motor Group's Supernal division represents South Korea's largest investment in urban air mobility technology. The S-A2 aircraft, unveiled in 2024, targets commercial passenger operations with advanced autonomous systems and integration with Hyundai's broader mobility ecosystem. Manufacturing facilities in South Korea leverage automotive-grade production capabilities while developing aviation-specific quality systems.
Korean Air's Urban Air Mobility division combines the national carrier's aviation expertise with eVTOL development, focusing on integration with existing airport infrastructure and air traffic management systems. Partnerships with international manufacturers including collaboration agreements with European and American eVTOL developers provide technology transfer opportunities while maintaining Korean manufacturing capabilities.
LG Electronics' contributions to urban air mobility include advanced avionics systems, communication technologies, and battery management systems that leverage the company's consumer electronics expertise for aviation applications. Samsung's involvement in 5G communication infrastructure and autonomous system development provides technological foundations for large-scale urban air mobility operations.
Infrastructure Development and Vertiport Planning
Seoul Metropolitan Area has advanced comprehensive vertiport planning through coordination between multiple government agencies and private sector partners. Gimpo Airport serves as a primary hub for urban air mobility development, with planned vertiports connecting to Incheon International Airport and multiple urban locations throughout the greater Seoul region.
Incheon Free Economic Zone provides regulatory flexibility for urban air mobility testing and early commercial operations. K-UAM Grand Challenge, South Korea's national urban air mobility demonstration program, coordinates between government agencies, manufacturers, and international partners to validate operational concepts and regulatory frameworks.
Digital infrastructure integration leverages South Korea's advanced telecommunications capabilities. 5G network coverage throughout major metropolitan areas enables real-time aircraft tracking, traffic management, and passenger services integration. Smart city initiatives in Seoul and Busan incorporate urban air mobility planning with broader digital infrastructure development.
Joint Development Programs and Regional Coordination
Japan-Korea cooperation in urban air mobility reflects broader technology partnership trends despite political complexities. Joint research programs between universities and research institutions in both countries focus on battery technology, autonomous systems, and air traffic management solutions applicable to dense urban environments.
ASEAN Plus partnerships include both countries in regional urban air mobility planning, coordinating regulatory approaches and infrastructure development across Northeast Asia. International standardization efforts through ICAO and other aviation organizations benefit from Japanese and Korean technical expertise and regulatory experience.
Market Preparation and Commercial Readiness
Japan's market approach emphasizes integration with existing transportation systems and gradual deployment beginning with specific use cases such as medical emergency services, disaster response, and tourism applications in remote areas. Aging population demographics create natural markets for air mobility services, particularly for healthcare access and emergency services in rural regions.
South Korea's urban focus targets metropolitan area congestion relief and airport connectivity services. Chaebol business model application to urban air mobility enables integrated service development combining aircraft manufacturing, infrastructure development, and operational services within single corporate structures.
Regulatory timeline coordination between both countries aims for initial commercial services in the late 2020s, though both governments maintain flexibility to adjust schedules based on safety validation results and public acceptance levels.
However, both countries face regulatory and cultural challenges that have influenced operational deployment compared to China's approach. The emphasis on consensus-building and risk management in both societies has resulted in more conservative approaches to technology deployment and regulatory approval, prioritizing thorough safety validation and public consultation over rapid scaling strategies.
Why Other Regions Face Challenges Matching Shenzhen's Development
The attempts by other global regions to replicate Shenzhen's development in low-altitude economy have revealed the challenges of implementing comprehensive strategies within different political, economic, and regulatory contexts. Understanding these challenges provides insights into the sustainability of Shenzhen's competitive advantages and the prospects for development in other regions.
Regulatory Fragmentation and Coordination Obstacles
The challenge faced by other regions attempting to emulate Shenzhen's development is the fragmentation of regulatory authority across multiple agencies and jurisdictions. In the United States, the division of authority between federal agencies, state governments, and local municipalities creates coordination challenges that affect the development of comprehensive low-altitude economy strategies.
The European Union faces similar challenges despite efforts to harmonize regulations across member states. The implementation of low-altitude economy policies remains largely a national responsibility, creating variations in regulatory approaches that complicate the development of region-wide strategies. Companies operating across multiple European countries must navigate different regulatory frameworks and approval processes, increasing costs and development timelines.
Market Structure and Economic Differences
The economic structure and market characteristics of other regions create challenges for replicating the demand density and operational scale achieved in Shenzhen. Most metropolitan areas outside China lack the combination of population density, manufacturing concentration, and logistics volume that creates conditions for low-altitude economy development.
The United States market, while large in absolute terms, is characterized by lower population density and more dispersed economic activity that makes it challenging to achieve the network effects and operational efficiency demonstrated in the Pearl River Delta region. American cities typically lack the cargo volume concentration that enables high-frequency drone delivery operations, requiring different business models and operational approaches.
European markets face similar challenges related to market fragmentation and lower demand density. While individual European cities may have sufficient population and economic activity to support low-altitude operations, the fragmentation across national boundaries limits the potential for developing integrated regional networks.
Lessons for Global Low-Altitude Economy Development
The analysis of Shenzhen's development and the challenges faced by other regions in replicating this development provides insights for stakeholders seeking to develop competitive positions in the evolving global low-altitude economy. Understanding these implications proves essential for companies, governments, and investors seeking to navigate this sector effectively.
Ecosystem Development Priority
Shenzhen's development demonstrates that competitive advantage in the low-altitude economy depends not solely on individual company capabilities but on the development of comprehensive ecosystems that support all aspects of the value chain. Regions seeking to develop competitive positions must invest strategically in building integrated ecosystems rather than focusing exclusively on attracting individual companies or developing specific technologies in isolation.
The development of supplier networks represents a critical component of effective ecosystem building. Regions must either develop local capabilities for critical components or establish reliable supply chain relationships that can support the rapid iteration and cost reduction required for commercial success. The advantages of local supplier networks become apparent during periods of rapid technology development when close collaboration between manufacturers and suppliers is essential for innovation.
Policy Framework Design and Implementation
The effectiveness of policy frameworks in supporting low-altitude economy development depends not merely on the content of policies but on the mechanisms for implementation and coordination across different agencies and jurisdictions. Regions must develop governance structures that enable rapid decision-making and coordinated implementation while maintaining appropriate safety and security standards.
Advanced Air Mobility companies require clear understanding of certification requirements, operational procedures, and liability frameworks to make informed investment decisions and develop sustainable business models. Regions that can provide this clarity quickly gain competitive advantages in attracting investment and development activities.
Future Outlook: Sustaining Global Leadership
As the low-altitude economy continues evolving from an emerging sector to a mainstream component of global transportation and logistics systems, the sustainability of Shenzhen's leadership position will depend on its ability to adapt to changing competitive dynamics while maintaining advantages in key areas and addressing emerging challenges and opportunities.
Shenzhen's current advantages in low-altitude economy development are based on early-mover advantages and the strategic integration of existing capabilities rather than fundamental technological breakthroughs that would be difficult for other regions to replicate. Sustaining leadership will require continued investment in research and development and the development of new capabilities that maintain competitive advantages as the sector matures.
The development of next-generation technologies including advanced autonomous systems, improved battery technology, and integrated traffic management systems represents areas where continued innovation will be important for maintaining global leadership. Shenzhen's research institutions and companies must continue pushing the boundaries of technological capability while other regions work to develop basic capabilities.
The development of international partnerships and joint ventures represents a strategy for accessing foreign markets while leveraging local capabilities and relationships. Chinese companies will need to balance the advantages of their integrated domestic ecosystem with the requirements for local adaptation and partnership in international markets.
The establishment of international standards and operational procedures represents both an opportunity and a challenge for Shenzhen's companies. Active participation in international standardization efforts could help establish Chinese approaches as global norms while also requiring adaptation to international requirements and diverse stakeholder concerns.
Shenzhen's transformation into a center of the low-altitude economy provides a case study in coordinated industrial development and strategic policy implementation. The city's development in achieving operational scale and commercial viability in low-altitude operations offers lessons for regions worldwide while highlighting both the opportunities and challenges inherent in this evolving sector. As the global low-altitude economy continues to mature, Shenzhen's experience will serve as both an inspiration and a benchmark for development efforts across the world.




