Hefei, the capital of Anhui Province in eastern China, has developed a broad low-altitude economy (LAE) industry base alongside other major Chinese cities, including Shenzhen. While Shenzhen usually gets the spotlight as China’s drone capital and low-altitude economy leader, Hefei has quietly built an extensive LAE ecosystem that rivals and, in some areas, surpasses the achievements of its more well-known counterpart.
Located in the heart of Anhui Province between the Yangtze and Huai Rivers, Hefei holds a strategic position in East China, roughly 130 kilometers west of Nanjing. The city has experienced impressive growth, with its population exceeding 8 million and serving as a major technological hub. This growth is mainly driven by talent migration, with over 91.8% of the population increase due to new residents moving in for opportunities in the city’s expanding technology industries.
Hefei’s demographic profile reflects a knowledge-based economy, with more than 180 researchers per 10,000 employed residents in 2023, which is twice the national average. The city also has an urbanization rate above 85%, supporting the infrastructure necessary for advanced air mobility activities.
Shenzhen: The Established Leader

Shenzhen’s reputation as China’s low-altitude economy capital is well-earned. The city hosts over 1,900 enterprises in the LAE sector, generating 21.38 billion yuan in value-added output with a 26.4% year-over-year growth. With global giants like DJI controlling 70% of the world’s consumer drone market, Shenzhen naturally draws international attention and media coverage.
The city’s achievements are impressive: over 700,000 cargo flights completed in 2024, more than 200 drone routes in operation, and plans to build over 1,200 takeoff and landing facilities by 2026. Shenzhen’s low-altitude economy reached an annual output of more than 90 billion yuan in 2024.
Shenzhen’s success comes from its strong culture of innovation and international business environment. The city’s characteristic “996” work culture, working from 9 AM to 9 PM, six days a week, fuels rapid development and gives companies like DJI a global leadership position. This demanding pace attracts young, ambitious professionals from across China and around the world, creating a lively talent pool willing to prioritize career growth over work-life balance.
The city’s cosmopolitan vibe and closeness to Hong Kong offer key advantages for entering international markets and integrating into global supply chains. However, this also leads to high housing costs, among the highest in China, which adds economic pressure and emphasizes the need for intense work schedules and high salaries. As a result, Shenzhen is especially appealing to career-driven individuals aiming for rapid professional growth in global markets.
Hefei: The Strategic Challenger

Hefei has developed an operationally focused urban air transport model that emphasizes practical urban air mobility applications. The city has gathered more than 300 companies involved in the low-altitude economy, creating what officials describe as a comprehensive ecosystem that integrates research and development, manufacturing, sales, operations, and service capabilities.
Hefei has prioritized operational deployment in medical logistics, emergency services, and daily urban applications. While Shenzhen excels in manufacturing and global market reach, Hefei has concentrated on building a functional urban air mobility system that addresses real daily needs.
Hefei’s approach reflects a fundamentally different development philosophy that emphasizes sustainable growth and practical implementation over fierce competition. The city’s significantly lower cost of living—with rental costs 75% less than Shenzhen—reduces financial pressure on workers and companies, allowing a focus on long-term growth rather than immediate market pressures.
This economic environment supports Hefei’s knowledge-intensive workforce, which includes a high number of researchers—twice the national average. The lower cost pressures foster more balanced workplace cultures that emphasize steady progress and collaborative innovation between public and private sectors. Instead of Shenzhen’s high-stakes, high-pressure environment for tech giants, Hefei’s government-supported initiatives promote innovation through stability and practical application, creating workplaces focused on solving real urban challenges via sustainable technological development.
The result is a city that attracts talent seeking professional growth in an affordable, balanced environment, while maintaining advanced skills in emerging technologies such as urban air mobility.
Luogang Central Park: One of the Largest Urban Air Mobility Hubs
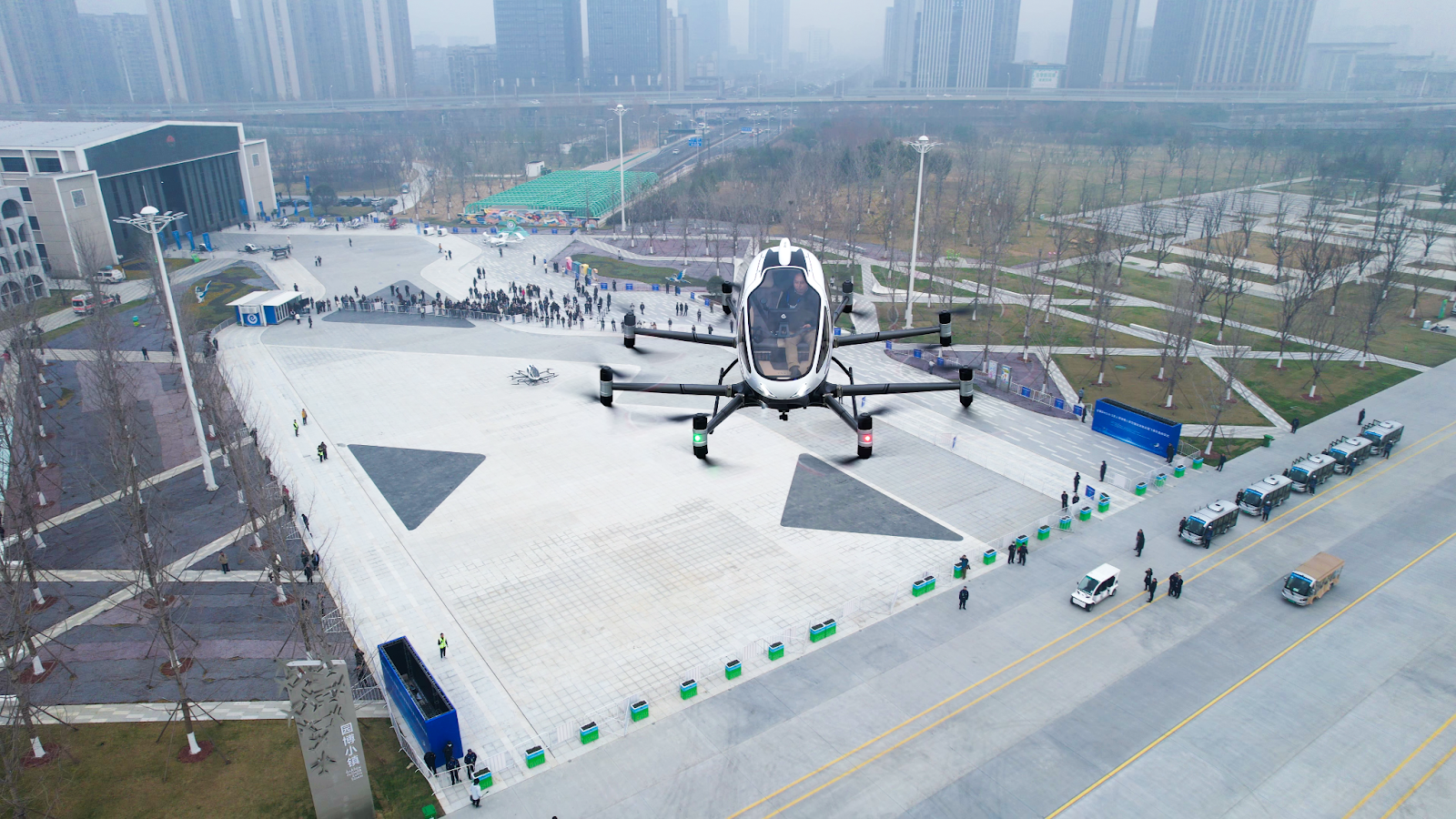 A single passenger flies in EHang’s autonomous air taxi above Hefei’s Luogang Central Park.
A single passenger flies in EHang’s autonomous air taxi above Hefei’s Luogang Central Park.
At the heart of Hefei’s low-altitude economy development is Luogang Central Park, a renovated 12.7-square-mile urban space built on the site of the former Hefei Luogang International Airport. This facility acts as a testing ground for urban air mobility operations. The park contains two major eVTOL operation centers formed through EHang’s partnership with the Hefei Municipal Government. These centers can support 10 units of EH216-S aircraft for operations and store up to 50 eVTOL aircraft, enabling low-altitude shuttle flights within the park. The Urban Air Mobility Operations Center, launched in May 2024, offers operational capacity for 10 units of EH216-S aircraft with space for up to 50 eVTOL aircraft.
This center facilitates low-altitude shuttle flights and serves as a testing ground for various UAM applications. The UAM Hub “Ascend,” launched in November 2024, features an upward spiral design symbolizing growth in the eVTOL low-altitude economy. It provides complete passenger services, including ticketing, waiting areas, boarding facilities, and maintenance operations. Hefei has built a comprehensive low-altitude operational network with over 100 service routes in seven different categories. These include: Medical Supply Delivery, with over 25 blood delivery routes connecting more than 20 hospitals across the city, reducing critical delivery times by more than 50%. Commercial Logistics, covering food delivery, package distribution, and emergency supply transport. Infrastructure Inspection, including rail track patrols, power line checks, and fire safety monitoring. Tourism and Sightseeing, offering commercial eVTOL flights for urban air mobility experiences.
Medical Emergency Networks
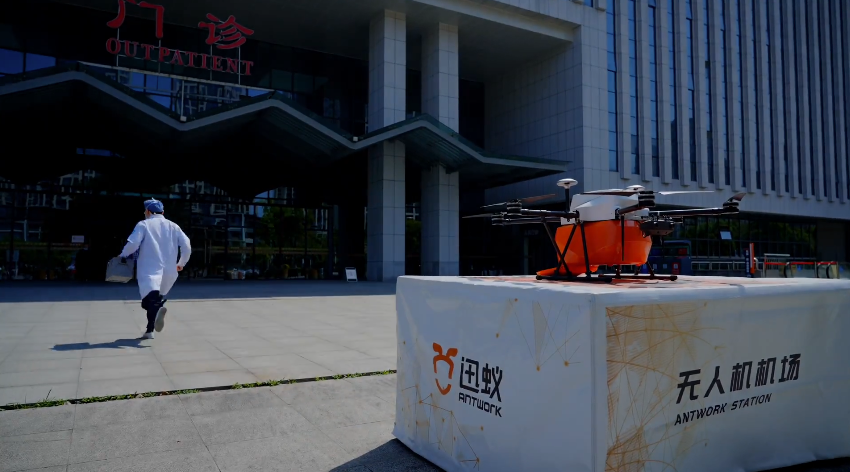

The city’s blood delivery network, operated by companies including Antwork Technology and Hefei Songba Feihe Low Altitude Logistics, demonstrates the practical applications of the low-altitude economy. These drones operate at approximately 100 meters altitude, covering about one kilometer per minute and providing critical medical supply transport that reduces delivery times by over half compared to traditional methods.
The city operates drone routes connecting 20 hospitals within 20-minute flight times, with daily medical flights growing from two to three flights to over 100 flights. This network has established close to 40 drone hubs throughout the city, specifically for medical logistics.
Hefei’s medical network demonstrates practical urban air mobility that directly saves lives, operating blood delivery systems that can transport over 10,000 milliliters of blood through multiple round trips during urgent situations.
Shenzhen, despite its larger scale, has not achieved this level of integration in critical emergency services.
Infrastructure Integration
Hefei operates over 200 drone corridors serving multiple applications, but more importantly, these corridors are integrated into the city’s broader transportation and emergency response systems. The city’s Luogang Park serves as both an operational hub and a “super experimental field” where visitors can access air taxi services and drone delivery operations.
Shenzhen’s 203 active drone routes and 121 dedicated takeoff and landing points represent impressive infrastructure, but Hefei’s integration approach creates more seamless user experiences and practical daily applications.
Hefei’s Vertiport UAM Infrastructure Network
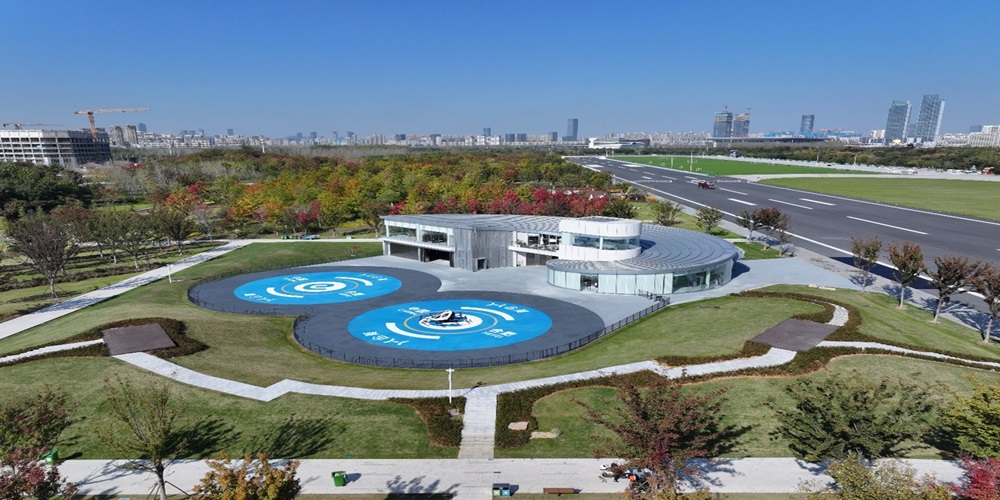 EHang UAM Hub in Hefei Luogang Central Park
EHang UAM Hub in Hefei Luogang Central Park
Hefei has developed a three-tier vertiport infrastructure network designed to support various urban air mobility applications. The city’s Low Altitude Infrastructure and Scenario Application Plan for Urban Air Mobility establishes a trilayer infrastructure network for low-altitude takeoff and landing based on specific application scenarios. The infrastructure features intelligent automation and innovative technology across all three tiers.
The Luogang facilities exemplify this innovation with automated vertical lift platforms that transport aircraft between floors, optimizing space and reducing labor costs. These systems enable quick aircraft deployment and efficient charging operations while seamlessly integrating takeoff and landing pads with hangar facilities. Each facility includes command-and-control centers that manage multiple aircraft operations and connect with the broader air traffic management system. This automated approach allows the network to handle growing operational demands while ensuring safety and efficiency.
UAM Hubs (Top Tier)
These large-scale facilities serve as primary operational hubs, exemplified by the Luogang Central Park complex. The flagship center covers approximately 1,963 square meters and can accommodate 10 to 20 EH216-S aircraft at the same time.
It includes extensive passenger service infrastructure with multiple dedicated zones for ticketing and waiting, along with specialized areas for boarding and departures. Operational management is centralized through command-and-control centers that oversee flight operations, ensuring coordinated and safe aircraft movements.
Aircraft support infrastructure forms a vital part of these facilities, including charging and maintenance areas designed for efficient fleet management. The hub also offers substantial storage capacity, capable of housing up to 50 eVTOL aircraft when not in use.
These facilities’ specifications demonstrate the scale of these top-tier operations: the roughly 1,963 square meter complex can handle 10 to 20 EH216-S aircraft simultaneously while providing storage for up to 50 eVTOL aircraft, establishing it as a major operational hub in the urban air mobility network.
UAM Bases (Secondary Tier)
These mid-sized facilities offer maintenance and operational support, acting as distribution points for drone operations and secondary hubs for passenger services. The UAM Bases complement the primary hubs by providing decentralized maintenance and regional coverage across Hefei’s urban area.
Takeoff and Landing Points (Tertiary Tier)
Distributed across urban areas, these smaller facilities serve as access points for low-altitude services. They allow for widespread coverage without requiring significant infrastructure investment at each site. The plan envisions these points supporting three main use cases: air shuttle services, aerial tourism, and cross-district transportation within the city’s central areas.
Key Companies and Partnerships
While Shenzhen benefits from proximity to Hong Kong and international markets, Hefei has utilized China’s regulatory framework more efficiently. Hefei Heyi Aviation became one of the first companies in China to obtain civil aviation permits for operating manned passenger drones, which the company calls “a passport to the sky.”
Anhui Province serves as a pilot area for China’s national low-altitude airspace management reform, giving Hefei regulatory advantages that even Shenzhen lacks. In March 2024, China’s civil aviation authority approved Anhui’s low-altitude expansion with 30 new airspace zones and 27 drone corridors in a single year.
Hefei’s low-altitude economy ecosystem includes over 100 companies involved in research and development, manufacturing, sales, operation, and service. The city has drawn significant industry players, including:
EHang Holdings Limited has built extensive operations in Hefei through a partnership with the municipal government, earning the world’s first type certificate for an autonomous passenger eVTOL (EH216-S) and conducting demo flights from Luogang Central Park.
Hefei Heyi Aviation, a joint venture with the government, received China’s first Air Operator Certificate for passenger drone services in March 2025, enabling urban sightseeing tours. In February 2025,
EHang announced a strategic partnership with JAC Motors and Guoxian Holdings to develop an eVTOL manufacturing plant, leveraging JAC’s automotive expertise.
Antwork, through Hefei Songba Feihe Low Altitude Logistics, has operated nearly 100 drone routes since February 2024, providing medical deliveries and managing the national drone operations center.
Market Position in National Context
Hefei consistently ranks among the 15 cities recognized for developing low-altitude economic ecosystems alongside Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Hangzhou. Even more notably, Hefei is one of only six cities—along with Shenzhen, Hangzhou, Suzhou, Chengdu, and Chongqing—selected as pilot cities for opening airspace below 600 meters. This places Hefei in the same exclusive group as Shenzhen for regulatory opportunities.
Economic Impact Projections
Hefei’s success challenges the idea that only established tech hubs like Shenzhen can lead in new industries. The city shows that strategic focus, government cooperation, and practical use can compete effectively with pure innovation and capital concentration.
While Shenzhen rightly gains recognition as China’s drone hub and pioneer of the low-altitude economy, Hefei’s detailed strategy for building functional urban air mobility systems offers a different yet equally valuable model for LAE development. The city’s focus on addressing real urban challenges through air mobility, rather than just advancing technology, provides valuable lessons for other cities worldwide aiming to develop practical low-altitude economy applications.





